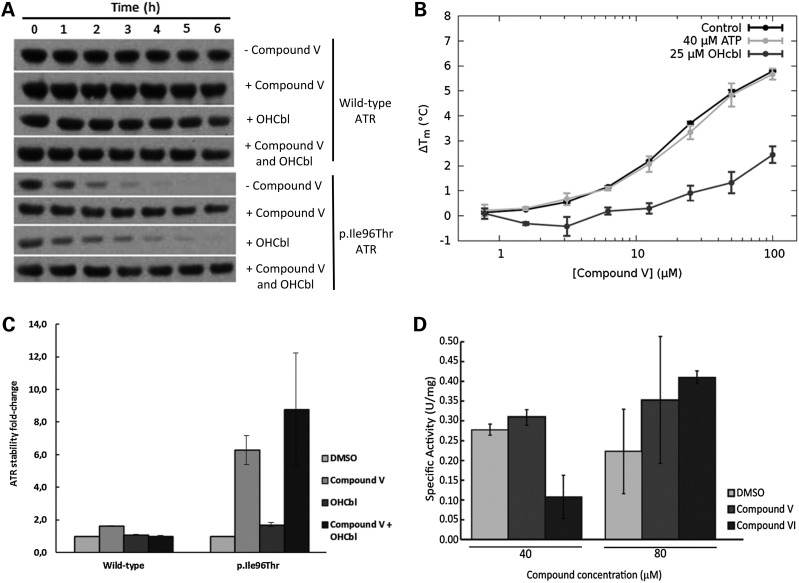
Figure 3.
Effect of compounds V, VI and cobalamin on ATR stability and activity. (A) Effect of compound V on p.Ile96Thr ATR protein stability. Bacteria expressing wild-type or p.Ile96Thr mutant ATR were incubated with 80 µm compound V (final DMSO concentration 0.2%) or the equivalent amount of the vehicle (0.2% DMSO) or with 1 µg/ml (0.7 µm) of OHCbl or both. Crude cell extracts from cultures expressing wild-type or p.Ile96Thr ATR were incubated at 37°C, and aliquots were removed at different times. The aliquots were loaded onto SDS–PAGE gels and the protein was immunodetected by western blotting. Proteins were quantified by laser densitometry as the percentage density of each protein relative to its density at time 0. Compound-treated samples were compared with the DMSO-treated sample. (B) Quantification of the effect of compound V and/or OHCbl on stability of wild-type ATR and mutant p.Ile96Thr ATR. (C) Concentration-dependent stabilization of ATR by compound V and effect of OHCbl and ATP. The stabilization of ATR in the presence of compound V (0–200 µm) in the absence of OHcbl (black solid line, circles) and in the presence of OHCbl at 3 µm (dark grey solid line, triangles) and 12 µm (light grey solid line, squares) or 40 µm ATP (dotted line, squares). See main text for estimated Kd values for compound V binding. (D) Specific activity was measured using purified wild-type ATR from bacteria with 40 or 80 µm of either compound V or VI or the equivalent volume of DMSO (final DMSO concentration 0.4 or 0.8%). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.