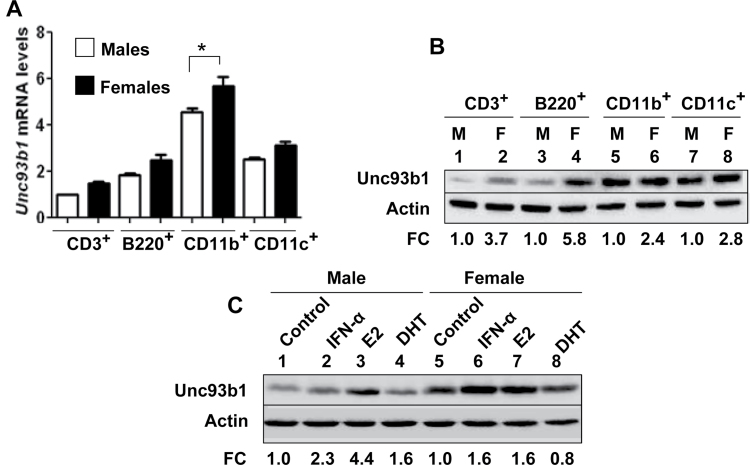
Fig. 1.
Steady-state levels of Unc93b1 mRNA and protein depend on the sex of mice and treatment of immune cells with estrogen or type I interferon increases the levels. (A) Total RNA from the indicated purified immune cells isolated from either C57BL/6 male (n = 4) or age-matched female (n = 4) mice was subjected to quantitative real-time PCR using the TaqMan assays specific to the murine Unc93b1 gene. The ratio of the Unc93b1 mRNA levels to β2-microglobulin mRNA was calculated in units (one unit being the ratio of the Unc93b1 mRNA to β2-microglobulin mRNA). The ratio of mRNA levels in CD3+ cells from male mice is indicated as 1. The error bars represent the standard deviation (*P < 0.05). (B) Total cell extracts from the indicated purified immune cells isolated from either C57BL/6 males (M; n = 4) or age-matched females (F; n = 4) were subjected to immunoblotting using antibodies specific to the indicated proteins. FC, fold change in the Unc93b1 protein levels is indicated. (C) Purified CD11b+ cells isolated from C57BL/6 male (n = 6) or age-matched female (n = 6) mice were either left untreated (control) or treated with IFN-α (1000U ml−1), 17β-estradiol (E2; 10nM) or DHT (10nM) as described in Methods for 18h. After the treatment, total cell extracts containing approximately equal amounts of proteins were subjected to immunoblotting using antibodies specific to the indicated proteins. FC, fold change in the Unc93b1 protein levels is indicated.