Fig. 3.
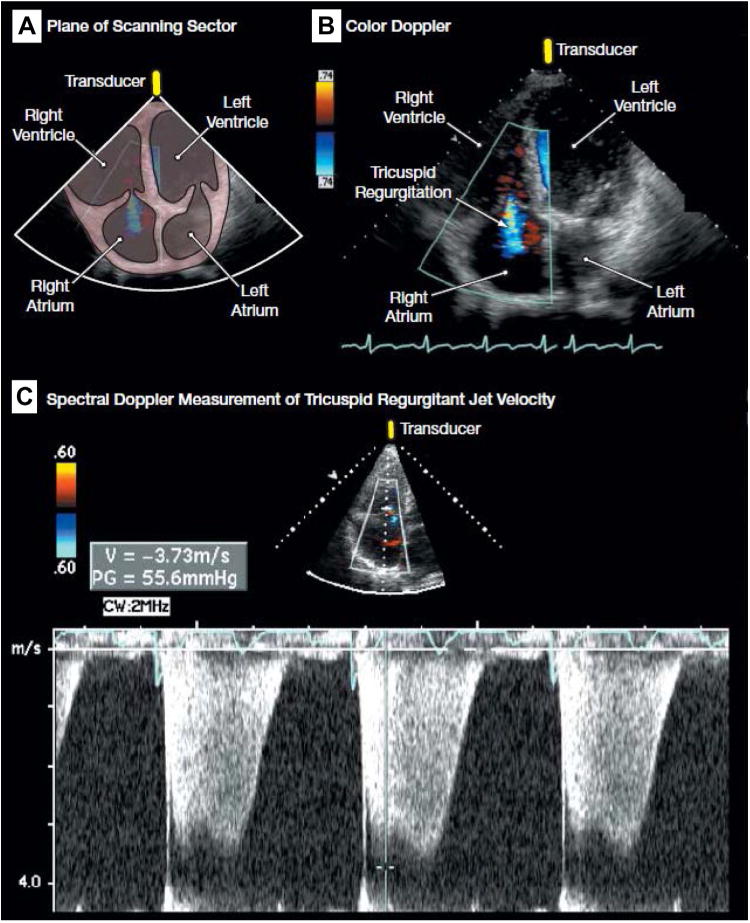
(A) Plane of scanning sector. (B) Color Doppler demonstrating tricuspid regurgitation (blue). (C) Spectral Doppler measurement of tricuspid regurgitant jet velocity for the estimation of pulmonary artery systolic pressure, demonstrating a peak tricuspid regurgitant jet velocity of approximately 3.7 m/s. Sampling of the peak tricuspid regurgitant jet velocity is used to estimate the RV to right atrial systolic pressure gradient (55.6 mm Hg in the figure) with the use of the modified Bernoulli equation (4 × [tricuspid regurgitant jet velocity]2). Pulmonary artery systolic pressure is quantified by adding the Bernoulli-derived pressure gradient to an estimate of mean right atrial pressure. (See video at http://jama.com/cgi/content/full/299/3/324/DC1.) (From Barnett CF, Hsue PY, Machado RF. Pulmonary hypertension. JAMA 2008;299:326; with permission.)
