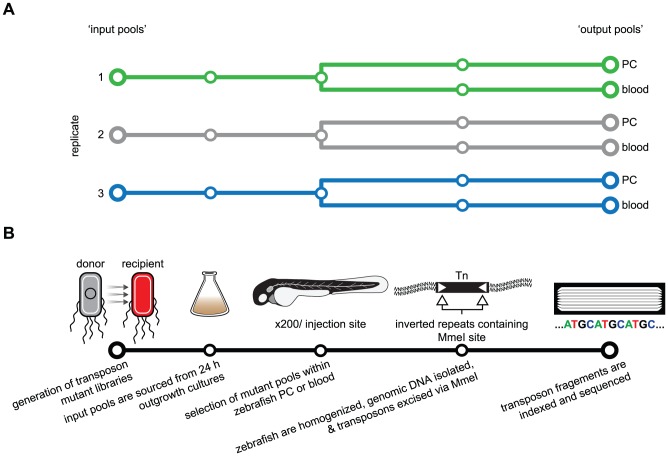
Figure 1. Schematic of the Tn-seq selection screen used to identify genes necessary for fitness in a zebrafish infection model.
(A) Three selection screens were performed (green, grey and blue tracks) using three ‘input’ pools to generate a total of six ‘output’ pools. (B) For each replicate screen, an independent transposon mutant library was created. Expansion of mutant libraries from frozen stocks was done at 37°C for 24 h to produce input pools and starting inoculum. Approximately 200 zebrafish embryos were injected in the pericardial cavity (PC) or circulation valley (CV, blood) with approximately 3,000 mutant bacteria. After a selection period of 20 h, zebrafish were homogenized to facilitate recovery and extraction of total DNA. The restriction enzyme MmeI was used to excise transposons and flanking F11 genomic DNA for analysis by deep sequencing.