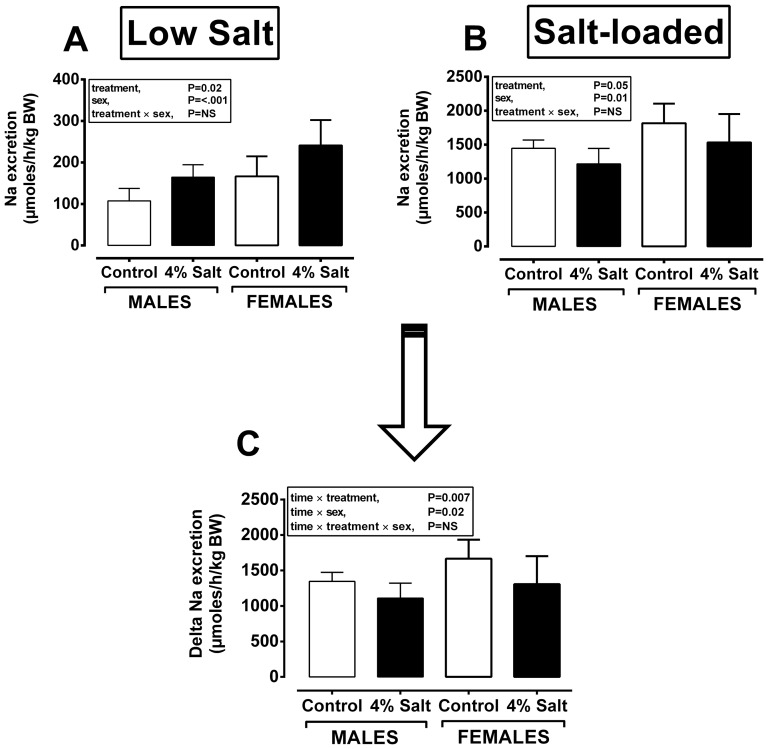
Figure 3. Salt-exposed offspring do not retain excess salt but have greater sodium excretion under low, but not high, salt-loading.
Na+ excretion were measured in 12 week old male and female offspring from dams fed control diet (Control, n = 12 dams; n = 9–12 males/females) or 4% salt diet with water ad libitum (4% Salt, n = 10 dams; n = 7–10 males/females). Paired plasma and urine were collected after 24 h in a metabolic crate after 5-days feeding either a low (0.26%; standard chow or LOW-SALT) or high-salt (4%; TD.08162, SALT-LOADED) diet. Data are means (±95% CI) and were analysed by mixed effect models with treatment (control vs. 4% salt) and sex (male vs. female) or their interaction as fixed and dam as a random effect (Genstat v14). NS, not significant.