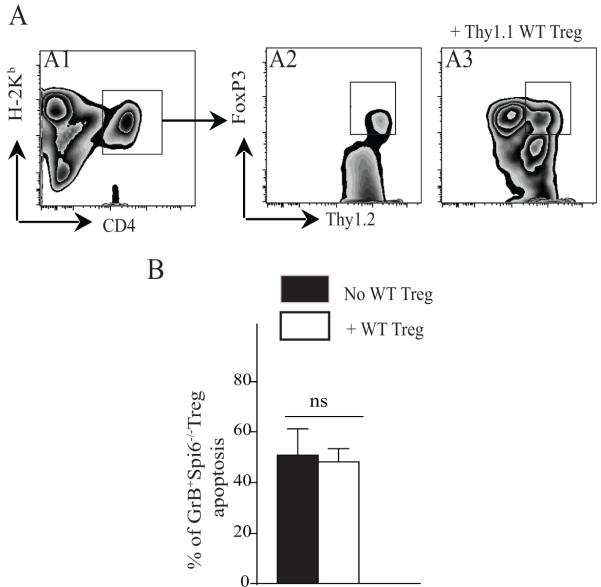
Figure 5. Adoptive Transfer of WT Tregs does not rescue GrB producing Spi6−/− Tregs from cell death.
(A) Representative example of flow cytometry gating on splenocytes derived from irradiated BALB/c mice reconstituted with T cells derived from WT (H-2Kb+thy1.2+) or Spi6−/− (H-2Kb+thy1.2+) mice and co-injected with WT (H-2Kb+thy1.1+) Tregs at 1/1 ratio. Control mice only received T cells without Tregs. Mice were sacrificed at day 10 post-adoptive transfer. Gating on Thy1.2 expression permits differentiation between induced Tregs (thy1.2+) and transferred WT Tregs (thy1.1+). A1 is a representative example of FACS staining of recipient splenocytes gated on H-2Kb+ and CD4+ (donor CD4+ T cells). A2 and A3 are representative examples of FACS staining of recipient splenocytes gated on H-2Kb+, CD4+, thy1.2+ and FoxP3+ (induced Tregs from donor CD4+T cells). A2 represents a mouse recipient of thy1.2+ T cells only. A3 represents a recipient mouse that received thy1.2+T cells in addition to WT thy1.1+Tregs. (B) Graph represents the percentage of apoptosis as measured by Annexin expression in induced Tregs from Spi6−/− T-cells, with or without co-transferred WT Tregs. Transfer of WT Tregs did not rescue induced GrB+ Tregs from accelerated cell death. (n=4-6 mice/group)