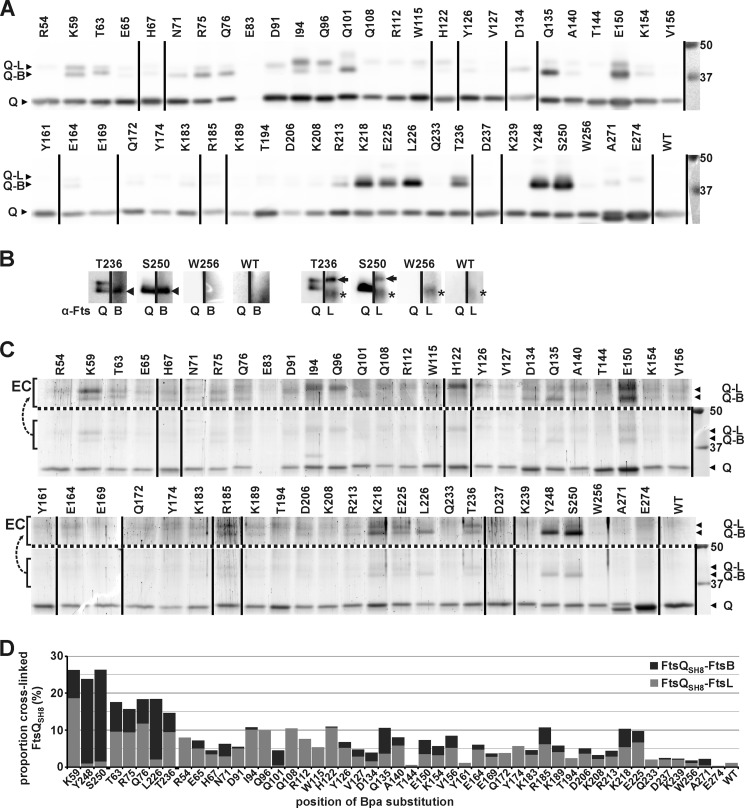
FIGURE 4.
Cross-links between FtsQSH8 and FtsB and FtsL. After exposure of cells expressing FtsB, FtsL, and an FtsQSH8 Bpa substitution mutant to UV, FtsQSH8 was purified under denaturing conditions. The residue substituted by Bpa is indicated. The sample from cells expressing the parental SH8ftsQ gene is indicated by WT. A, detection by Western blotting using FtsQ-specific antibodies. Full-length FtsQSH8 and Bpa variants (Q) and two adducts, identified in B as FtsQSH8-FtsB (Q-B) and FtsQSH8-FtsL (Q-L), were detected. B, detection by Western blotting using FtsQ-specific antibodies (α-FtsQ) on one half of a lane and FtsB-specific antibodies (α-FtsB) or FtsL-specific antibodies (α-FtsL) on the other half of the same lane to identify the two adducts recognized by α-FtsQ. The FtsQSH8-FtsB adduct (arrowhead), the FtsQSH8-FtsL adduct (arrow), and an aspecific signal (asterisk) are indicated. C, to crudely quantitate the amounts of full-length FtsQSH8, FtsQSH8-FtsB and FtsQSH8-FtsL, the proteins separated by SDS-PAGE were stained with colloidal Coomassie. The proteins are indicated as in A. To enhance the visibility of the adducts, the region containing these proteins is duplicated above the dotted line with enhanced contrast (EC). The lower region of these gels showing truncated FtsQSH8 as well as full-length FtsQSH8 is shown in supplemental Fig. S2. D, from the crude quantitation of the amounts of FtsQSH8, FtsQSH8-FtsB, and FtsQSH8-FtsL, the proportion of cross-linked FtsQSH8 was calculated. The proportion is divided into FtsQSH8-FtsB and FtsQSH8-FtsL, which are indicated in dark gray and light gray, respectively. In A and C, two identically treated Western blots and two identically treated gels, respectively, were combined, and the lane order was rearranged as indicated by vertical lines. On the right, the protein standard and corresponding molecular weight (kDa) are shown.