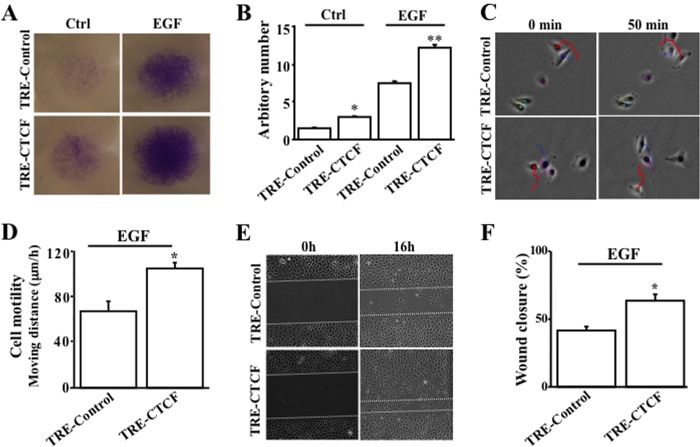
FIGURE 6.
Effect of NFκB-controlled CTCF activity on EGF-induced wound healing. A, effect of NFκB-controlled CTCF activation on EGF-induced cell migration. B, significant increase in migration by EGF-induced and NFκB-controlled CTCF activation. HTCE cell migration was measured by transwell migration assays. * and **, p < 0.05 between the TRE-control and TRE-CTCF groups in the absence and presence of EGF, respectively (n = 4). C, EGF-activated cell motility enhanced by NFκB-controlled CTCF activation. D, statistical significance of motility increase by NFκB-controlled CTCF activation in EGF-induced cells. HCE cell motility was measured by using the cell tracking function of a Nikon fluorescent microscope. *, p < 0.05 between the TRE-control and TRE-CTCF groups in response to EGF stimulation (n = 86). E, EGF-activated wound closure enhanced by NFκB-controlled CTCF activation. F, statistical significance of accelerated wound closure by NFκB-controlled CTCF activation in EGF-induced cells. HCE cell wound closure was measured by a scratch-induced directional wound healing assay. *, p < 0.05 between the TRE-control and TRE-CTCF groups in response to EGF stimulation (n = 4).