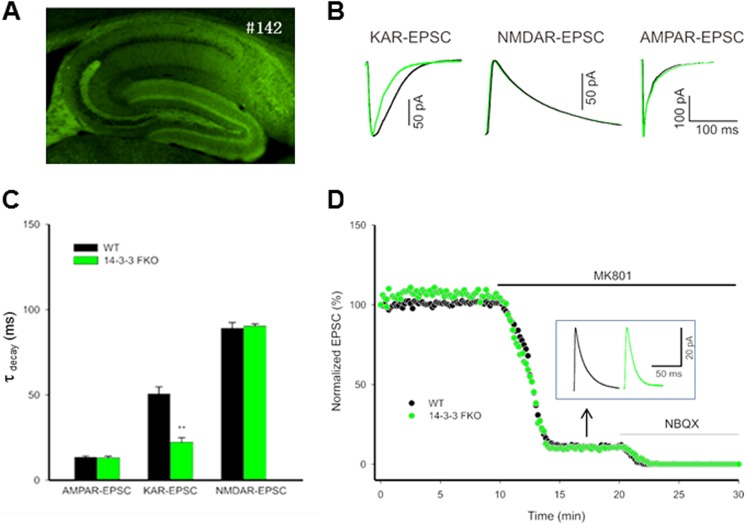
FIGURE 8.
14-3-3 proteins modulate the kinetics of KAR-mediated synaptic currents. A, fluorescence image of hippocampal slice from the 14-3-3 FKO mice. #142 refers to the founder line that has extensive expression of the transgene (YFP-fused R18 dimer) in specific regions of the hippocampus. B, representative normalized KAR-, NMDAR-, and AMPAR-mediated EPSCs recorded from the 14-3-3 FKO mice (green trace) and their wild-type littermates (dark trace). KAR-EPSCs decay faster in 14-3-3 FKO mice compared with the wild type (left), but there is no difference between 14-3-3 FKO mice and their wild-type littermates in NMDAR-mediated EPSCs (elicited by mossy fiber stimulation; middle), and AMPAR-mediated EPSCs (elicited by stimulation of associational/commissural fibers; right). C, comparison of the decay time constants for KAR-, NMDAR-, and AMPAR-mediated EPSCs, measured by single exponential fit to the decaying phase of the currents. (n = 4, **, p < 0.01). D, representative example of KAR- and NMDAR-EPSCs. Mossy fiber-evoked mixed KAR responses were recorded at +30 mV in the presence of AMPAR blocker. After establishing a base line, 50 μm MK-801 was washed in to isolate pure KAR-EPSCs. Inset traces show the residual KAR-EPSCs after MK-801 block. Green and dark traces are from the 14-3-3 FKO mice and their wild-type controls, respectively.