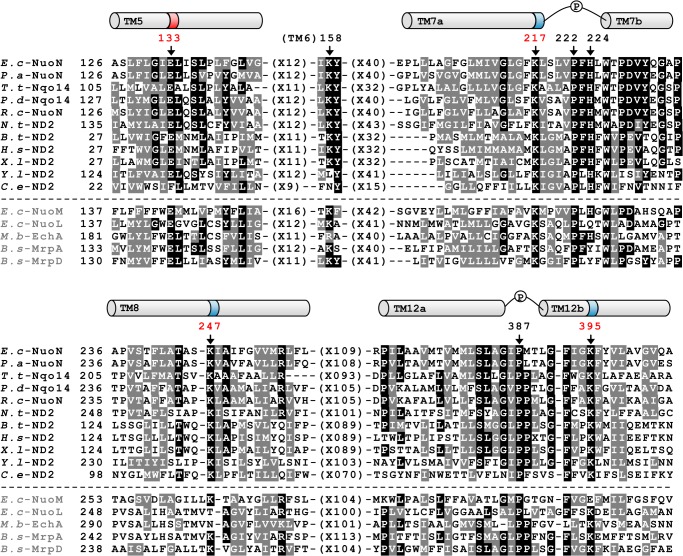
FIGURE 1.
Comparison of the amino acid sequences among the NuoN (ND2) subunits and other homologous antiporters. The alignment around helices that contain conserved charged residues presumably involved in H+ translocation was carried out by using the Clustal W program (54). Helices are depicted above the alignment based on the three-dimensional structure of E. coli NuoN (17), highlighting the candidates of essentially charged residues for energy-coupled NDH-1 activities (dark colored) and prolines in discontinuous helices (P). Black boxes with white letters show identical residues, whereas dark gray boxes with white letters illustrate similar residues among at least eight listed organisms. Dashes represent gaps to facilitate alignment. Amino acids mutated in this study are marked by arrows with the numbering in E. coli NuoN. Sequence sources and their UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot accession numbers are: E.c-NuoN, E. coli K-12 NuoN subunit (P0AFF0); P.a-NuoN, Pseudomonas aeruginosa NuoN subunit (Q9I0I9); T.t-Nqo14, Thermus thermophilus Nqo14 subunit (Q56229); P.d-Nqo14, Paraccocus denitrificans Nqo14 subunit (A1B479); R.c-NuoN, Rhodobacter capsulatus NuoN subunit (P50973);, N.t-ND2, Nicotiana tabacum GN Nad2 subunit (Q5MA39); B.t-ND2, Bos taurus ND2 subunit (P03892); H.s-ND2, Homo sapiens ND2 subunit (B1NU62); X.l-ND2, Xenopus laevis ND2 subunit (P03894); Y.l-ND2, Yarrowia lipolytica ND2 subunit (Q9B6C8);, C.e-ND2, Caenorhabditis elegans ND2 subunit (P24889); E.c-NuoM, E. coli K-12 NuoM subunit (P0AFE8); E.c-NuoL, E. coli K-12 NuoL subunit (P33607); M.b-EchA, Methanosarcina barkeri EchA subunit (O59652); B.s-MrpA, Bacillus subtilis MrpA subunit (Q9K2S2); B.s-MrpD, B. subtilis MrpD subunit (O05229).