Figure 2.
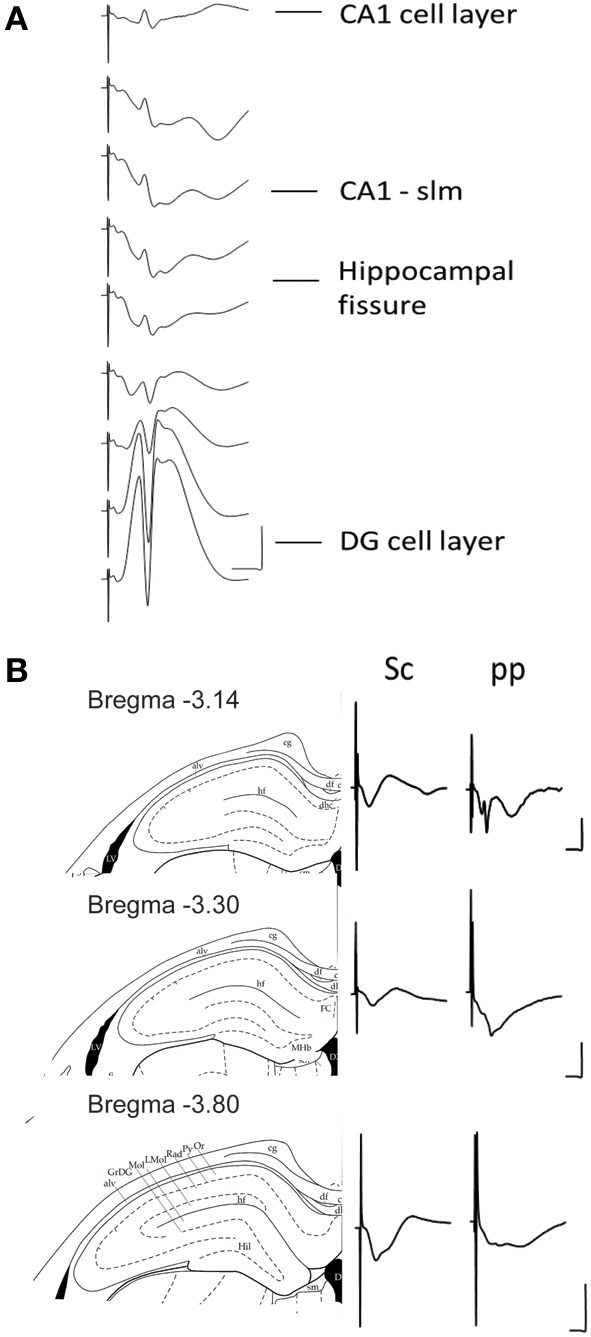
(A) Depth profile of evoked potentials as a result of perforant path stimulation. Example of typical field responses in vivo evoked by perforant path stimulation. The recordings started at the granule cell layer of the dentate gyrus (DG). The depth was decreased stepwise at 5 min intervals progressing “backwards” to the CA1 region. The distance between each representative recording was 160 μm. The stimulation intensity for all recordings was 200 μ A. Vertical scale bar: 5 mV, horizontal scale bar: 3 ms. (B) Evoked potentials at the CA1-stratum lacunosum moleculare synapse in response to Schaffer collateral and perforant path stimulation. Examples of typically evoked responses in vivo at the CA1-slm as a result of Schaffer collateral (analogs on the left) and perforant path stimulation (analogs traces on the right) at three different anterioposterior coordinates. The diagrams to the left of the analog traces represent coronal sections of hippocampal formation −3.14 mm (Top), −3.30 mm (middle), and −3.80 mm (bottom) from bregma (Paxinos and Watson, 1998). The histological examination of the recording site was depicted as a dot on the corresponding slide (Paxinos and Watson, 1998). All of the recordings were taken from freely behaving rats. The stimulation intensity for all recordings was 200 μ A. Vertical scale bar: 5 mV, horizontal scale bar: 5 ms for all traces. alv, alveus of the hippocampus; cg, cingulum; df, dorsal fornix; FC, fasciola cinereun; GrDG, granular layer of the dentate gyrus; hf, hippocampal fissure; Hil, hilus of the dentate gyrus; LMol, lacunosum moleculare layer of the hippocampus; Mol, molecular layer of the dentate gyrus; Or, oriens layer of the hippocampus; Py, pyramidal cell layer of the hippocampus; Rad, stratum radiatum of the hippocampus.
