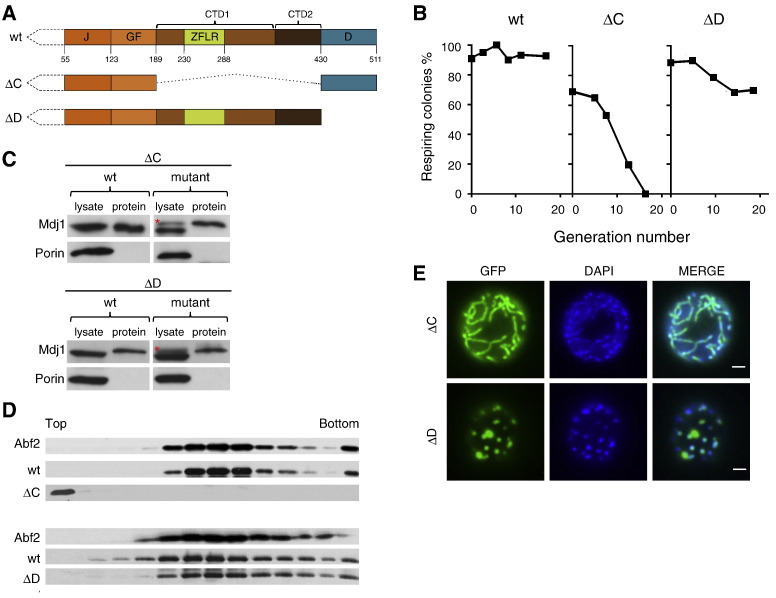
Fig. 4.
CTD1/2 domains of Mdj1 are critical for maintenance of mtDNA. A) Scheme of domain composition of Mdj1 deletion variants as in Fig. 3A. Internal deletion of Mdj1ΔC is indicated by dotted line. B) mdj1-Δ [TETr-MDJ1] expressing Mdj1 (wt), Mdj1ΔC (∆C) or Mdj1ΔD (∆D) under control of the MDJ1 promoter was grown in the presence of doxycycline. At the indicated number of generations after doxycycline addition, aliquots were collected and plated on glucose-based media. The percentage of respiring cells was taken as the ratio of the number of red colored versus the total number of colonies. C) Mitochondrial lysates were prepared from cells harvested 10 generations after doxycycline addition and subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies specific for Mdj1 and, as loading control, porin. As a quantity reference 0.2 pmol of purified wt Mdj1 (wt), Mdj1ΔC (∆C) or Mdj1ΔD (∆D), was run on the same gel (protein), as the polyclonal Mdj1 antibody does not recognize Mdj1, Mdj1ΔC and Mdj1ΔD with the same efficiency. Slower migration of the purified ΔC and ΔD variants is due to the presence of 6 His tag at the C-terminus. Red star indicates unspecific bands. D) Distribution of Mdj1 variants after centrifugation of mitochondrial lysates. Mitochondrial lysates isolated from MDJ1/mdj1-Δ diploid cells expressing wt Mdj1 (wt) or the variants, Mdj1ΔC (∆C) or Mdj1ΔD (∆D) were subjected to ultracentrifugation through a sucrose gradient. Each fraction was analyzed for protein content using immunoblot analysis with antibodies specific for Mdj1 or, as a control, Abf2. E) Cellular localization of Mdj1 variants. Cells expressing GFP fused to Mdj1ΔC (∆C) or Mdj1ΔD (∆D) were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Cellular DNA was stained with DAPI. Overlay of the two images (MERGE). Size bars (2 μm) are shown.