Figure 1.
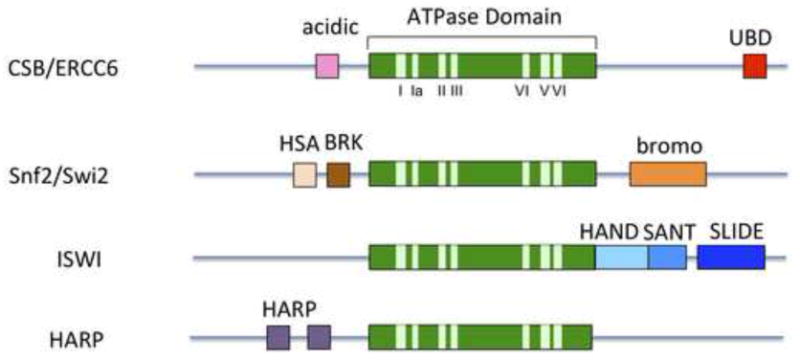
Representative SWI2/SNF2 ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling family members. The central ATPase domain (green) consists of seven conserved helicase motifs (light green) and is the most conserved region among family members. The CSB remodeler contains an acidic-rich region of unknown function and a ubiquitin-binding domain (UBD). Some remodelers have additional domains in their N- or C-terminal regions that are involved in mediating specific chromatin interactions or remodeler function. For example, the bromo domain has an increased affinity for acetylated proteins, including acetylated histones. The HAS domain has been found to mediate interactions with nuclear actin-related proteins (ARPs) as well as actin. The function of the HAND domain is still unclear, but it may be important for histone H3 tail binding (Grüne et al., 2003). The SLIDE domain appears to be important for DNA binding and ATPase activity and together, the SANT and SLIDE domains are likely important for nucleosome interaction. The HAPR domain dictates ATP-dependent annealing helicase activity (Ghosal et al., 2011). The BRK domain is of unknown function.
