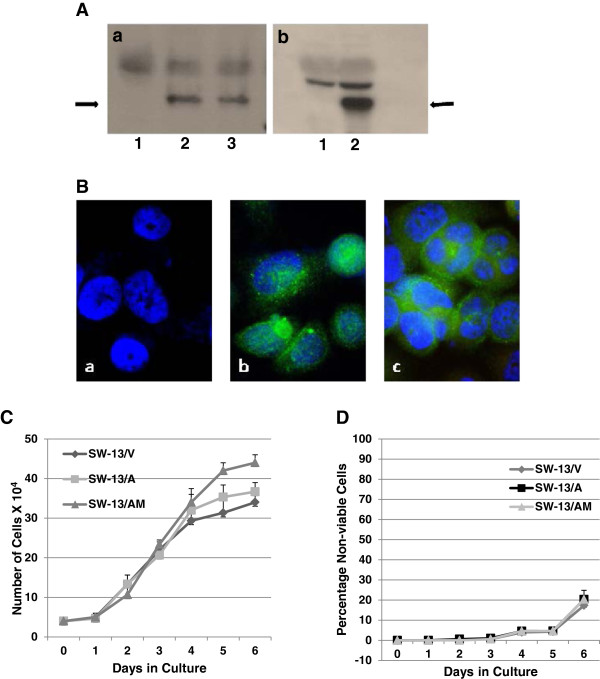
Figure 4.
Stable expression and selection of RASSF1A-expressing ACC cell lines. SW-13 ACC cells were transfected with CMV-promoted RASSF1A and RASSF1A/A133S mutant genes and G-418 resistant clones were selected under low-seeding densities. Multiple clones were pooled to make populations to avoid variability in expression levels. (A) Western Immunoblot detection of RASSF1A and RASSF1A/A133S (arrows point to the RASSF1A bands) expression using anti-DDK (a) or anti-RASSF1A (b) antibody (lanes a1: transfected with empty vector; lane a2: RASSF1A; lane a3: RASSF1A/A133S; b1 empty vector, and lane b2 RASSF1A expression vectors). (B) Immunofluorescence detection of RASSF1A expression in (a) SW-13/N, (b) SW-13/A, and (c) SW-13/M cells, using anti-RASSF1A mAb followed by anti-mouse-FITC antibody (green). DAPI stained nucleus appears blue. (C &D) Established populations were grown for 7 days to determine the effect of constitutive expression of RASSF1A or RASSF1A/A133S on proliferation (C) and survival (D) in comparison to vector-transfected and selected cells. Graphs represent data from one of two independent experiments with similar results.