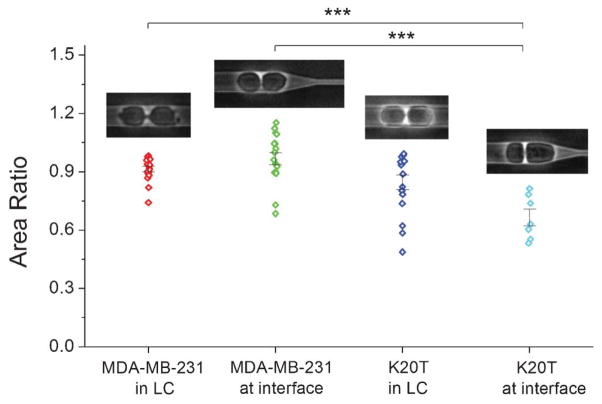
Fig. 6.
Cell division asymmetry. MDA-MB-231 cells tend to divide symmetrically both in the larger channel LC and at the barrier interface. K20T cells, however, tend to divide asymmetrically at the subnucleus barrier interface. The daughter cell closer to the barrier is larger. AR = area ratio between daughter cells. In the symmetric larger channel LC, AR = smaller cell/larger cell. At the interface, AR = left cell/right cell, and only cells dividing while invading from left to right into the SNB are taken into account. The area ratios measured are (mean = 0.91, median = 0.92, n = 19) for MDA-MB-231 in LC, (mean = 0.97, median = 0.96, n = 17) for MDA-MB-231 at SNB interface, (mean = 0.85, median = 0.94, n = 17) for K20T in LC, and (mean = 0.67, median = 0.63, n = 7) for K20T at SNB interface. *** indicates p < 0.001 from ANOVA statistics. Error bars are s.e.m. The width of the larger channel is 15 μm.