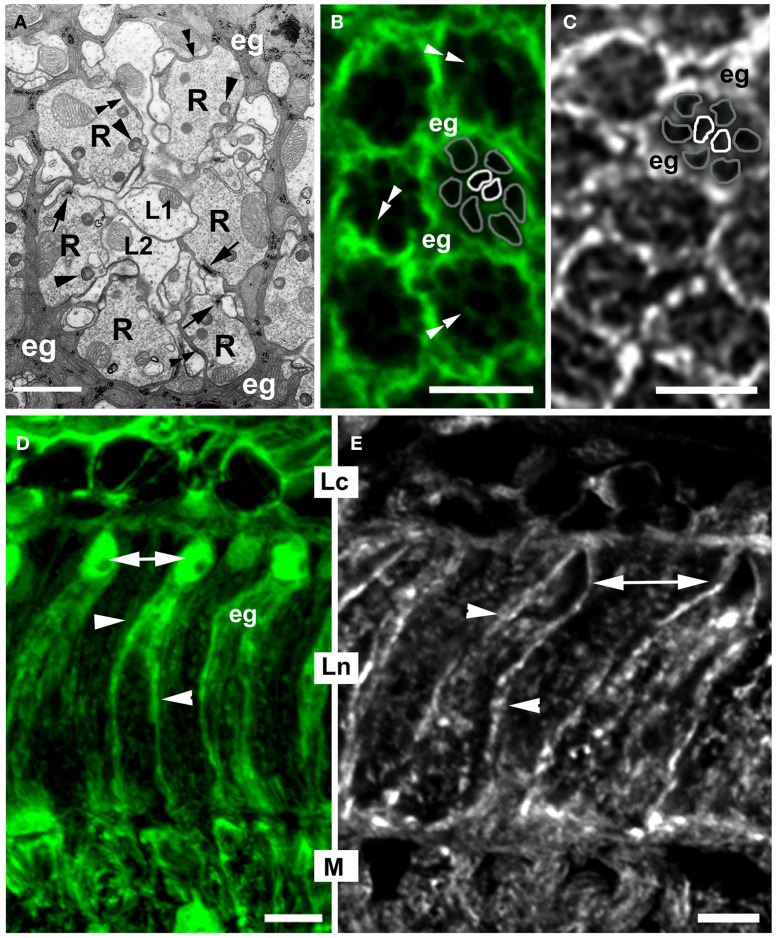
Figure 2.
The morphology of the cartridge in cross- (A–C), and longitudinal (D,E) section of Drosophila melanogaster first visual neuropil or lamina. (A) EM microphotograph of a single cartridge. The cylindrical terminals of six photoreceptors (R) surround axons of their main target cells, the L1 and L2 lamina interneurons, the so called large monopolar cells (LMCs). Apart from these, each cartridge hosts also smaller processes (not marked) of two more photoreceptors, R7 and R8, and three other monopolar cells, L3–L5, as well as profiles of amacrine cells, whose cell bodies are located in the second visual neuropil or medulla, and tangential neurons with cell bodies in other parts of the brain. Each cartridge is enwrapped by three cells of epithelial glia (eg) that send small processes into the cartridge (double arrowheads) and deep, dynamic invaginations with a spherical head, called capitate projections (arrowheads) into photoreceptor terminals. R-terminals contain profiles of presynaptic ribbons (T-bars) of the tetrad synapses (arrows), the most abundant type of synapses in the lamina. They constitute approximately 59% of the total number of all synapses of a cartridge (Meinertzhagen and Sorra, 2001). These synapses transmit photic and visual information received by ommatidia toward the brain. Scale bar: 1 μm. (B) Confocal image of the cartridges of Repo-Gal4 × UAS-S65T-GFP transgenic flies. GFP labels the epithelial glia (eg) surrounding cartridges. There are also visible thin processes (double arrowheads) invading the cartridge. One of the cartridges contains schematic representation of its main components, namely the terminals of R1–R6 photoreceptors (gray outline) and the axons of L1, L2 monopolar cells (white outline). Scale bar: 5 μm. (C) The pattern of α5 Mab (Hybridoma) immunolabeling of Na+/K+-ATPase α-subunit in the cartridges of lamina. The strongest signal comes from the epithelial glia (eg). As in (B), one of the cartridges contains schematic representation of R1–R6 terminals (gray outline) and the axons of L1 and L2 (white outline). Scale bar: 5 μm. (D) GFP fluorescence in the lamina glial cells of Repo-Gal4 × UAS-S65T-GFP transgenic flies. Epithelial glia (eg) are localized in the synaptic part of the lamina (Ln). Their cell bodies with nuclei (arrows) are located in the distal part of the neuropil, whereas their processes (arrowheads) reach the proximal part of the neuropil. Lc, lamina cortex; M, medulla. Scale bar: 5 μm. (E) Immunoreactivity to the α-subunit of the Na+/K+-ATPase in the longitudinal section of lamina. Similarly as in the lamina cross section (C), the strongest fluorescence is visible in the membrane of cell bodies (arrows) and processes (arrowheads) of the epithelial glia. Scale bar: 5 μm.