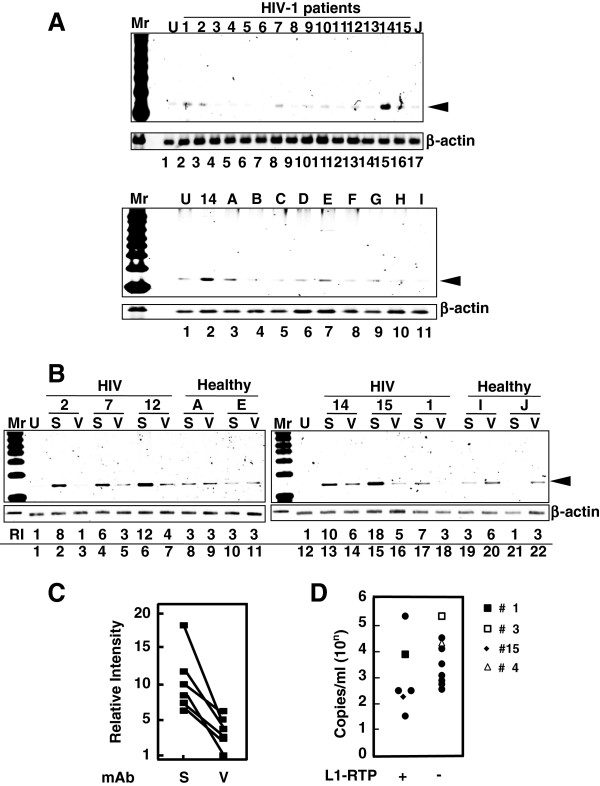
Figure 2.
Detection of Vpr-induced L1-RTP in blood samples of HIV-1-positive patients. A. Upper panel. Activity for the induction of L1-RTP in the blood of HIV-1-positive patients. Results of the PCR-based assay were shown. Lower panel. As a control, samples of nine healthy volunteers were included (A–I). U, Untreated. B. A mAb against Vpr blocked the activity in serum samples. Serum sample of 300 μL was treated with ~500 ng 8D1 (V) or SARS-mAb (S). Serum samples from healthy volunteers were also included (Healthy, A, E, I and J). RI, relative intensity. C. Effects of 8D1 on the activity of L1-RTP. RI shown in Figure 2B was plotted and compared. S, treatment with a mAb to SARS; V, 8D1. 8D1 considerably attenuated the L1-RTP-inducing activity in the patients’ blood. D. Detection of Vpr-induced L1-RTP in patients with lower viral titres with (+) or without (−) L1-RTP activity. According to the presence of the activity of L1-RTP in blood, patients were separated into two groups. Then, viral loads of each patient were plotted. Blood samples of two patients of each group were subjected to the IP-WB analysis. Vpr was detected in one patient (no. 15, ◆) (Additional file 5: Figure S4). Vpr was not detected in the sample of patient no. 1 (■), who was positive for L1-RTP. Other two patients were negative for both the activity of L1-RTP and Vpr (patient no. 3 and 4, □ and △).