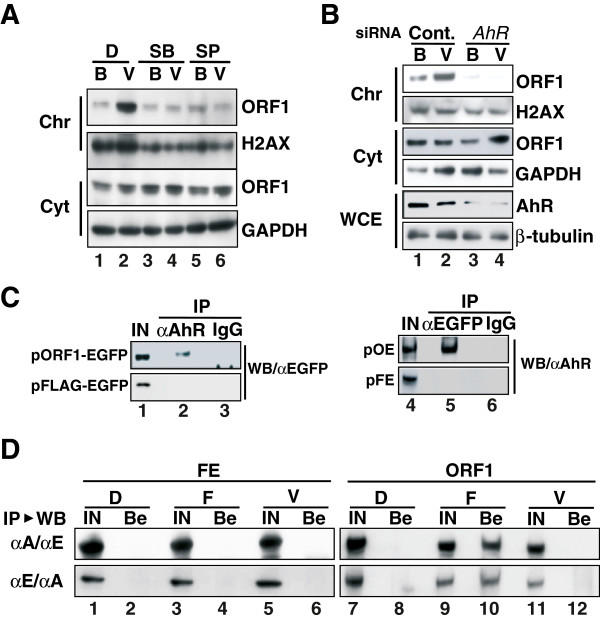
Figure 7.
rVpr-induced chromatin recruitment of ORF1. A. Chromatin recruitment of ORF1 is dependent on MAPK. HuH-7 cells were transfected with pORF1-TAP, and then WB was performed using a peroxidase-conjugated human IgG, α-H2AX and α-GAPDH. Cellular fractions of chromatin (Chr) and the cytoplasm (Cyt) were analyzed. D, DMSO; SB, SB202190; SP, SP600125; B, buffer; V, rVpr (5 ng/mL). B. AhR siRNA blocked rVpr-induced ORF1 chromatin recruitment. After transfection of AhR siRNA, similar experiments to those shown in Figure 7A were conducted. Chr, chromatin fraction; Cyt, cytoplasmic fraction; WCE, whole-cell extracts; B, buffer; V, rVpr. See also Additional file 13: Figure S11 showing results of independent experiments done using a different AhR siRNA. C. Association of AhR and ORF1. HuH-7 cells were transfected with constructs expressing a chimeric protein of ORF1 and EGFP (pORF1-EGFP) or a FLAG-tagged EGFP (pFLAG-EGFP). IP-WB was then performed using α-AhR followed by WB using α-EGFP (lane 2). As a reverse experiment, IP using α-EGFP was performed followed by WB using α-AhR (lane 5). D. rVpr induced no association of ORF1 and ARNT1. HuH-7 cells were transfected with pFLAG-EGFP (FE) (lanes 1–6) or pORF1-EGFP (ORF1) (lanes 7–12). After treatment of cells with rVpr (lanes 5, 6, 11, and 12) or FICZ (lanes 3, 4, 9 and 10), IP followed by WB were performed using α-ARNT1 and α-EGFP, respectively (upper panels). As a reverse experiment, IP using α-EGFP followed by WB using α-ARNT1 were performed (lower panels). D, DMSO; F, FICZ (10 nM); V, rVpr (5 ng/mL); IN, input; Be, fraction recovered using protein-G beads.