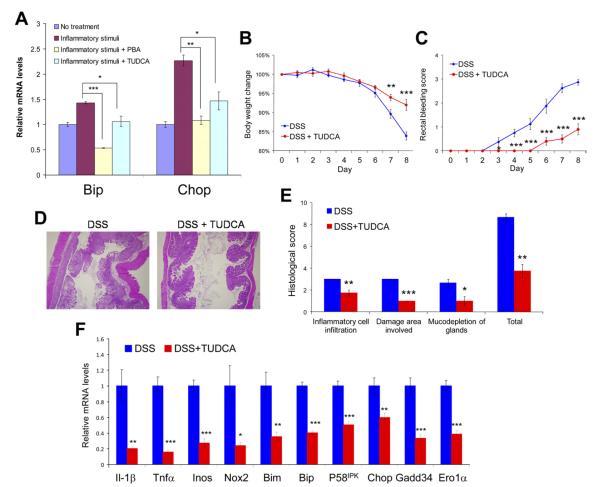
Figure 3.
TUDCA and PBA alleviate inflammatory stimuli-induced ER stress in IECs in vitro; TUDCA ameliorates DSS-induced colitis by reducing ER stress in colonic epithelium in vivo. (A) IEC-6 cells were treated with a combination of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, MCP-1, and IL-1β) for 8 hours or pretreated with 5 mmol/L TUDCA or PBA for 4 hours, followed by treatment with the same inflammatory signals with 5 mmol/L TUDCA or PBA for 8 hours. The cells were then collected for RNA extraction and quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. The messenger RNA levels were normalized to the expression of 18S ribosomal RNA. Wild-type mice were fed 2.5% DSS in drinking water and received 500 mg/kg body wt TUDCA or the same amount of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) without TUDCA daily by gavage (n = 8 or 10 per group). (B) Body weight and (C) rectal bleeding were measured over 8 days. (D) After administration of DSS, the colons were isolated and fixed for H&E staining. Representative images are shown (original magnification 40×). (E) Histologic scores are shown from TUDCA-treated and control mice with DSS-induced colitis. (F) Expression of genes associated with inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in colonic mucosa as well as ER stress markers in colonic IECs is shown (normalized to the expression of Gapdh). n = 8 for each group; *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001.