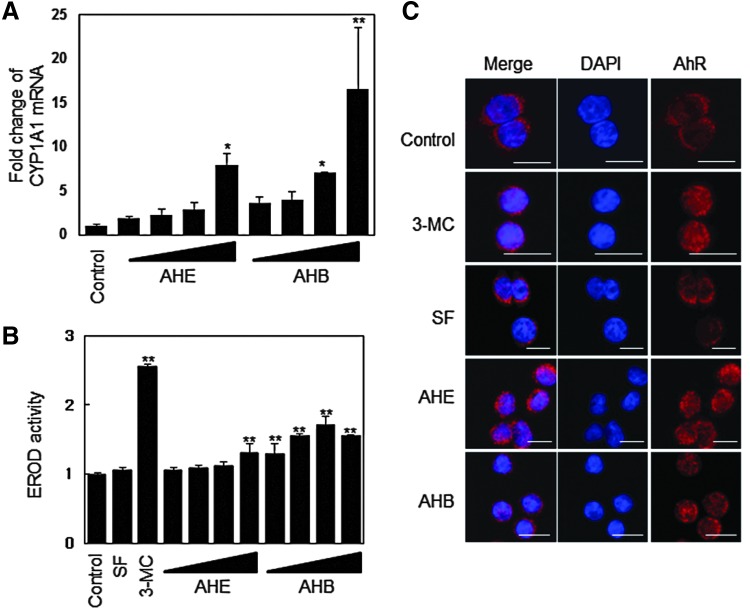
FIG. 5.
The AHE and AHB increase CYP1A1 mRNA levels and induce EROD activity by inducing AhR accumulation in the nucleus. (A) CYP1A1 mRNA expression in response to treatment with the AHE or AHB in HCT116 cells. HCT116 cells were treated with 25, 50, 100, and 200 μg/mL of the AHE or AHB for 24 h. (B) EROD activity in response to treatment with the AHE or AHB in Hepa1c1c7 cells. 3-MC (0.1 μM) was used as a positive control. HCT116 cells were treated with 25, 50, 100, and 200 μg/mL of the AHE or AHB for 24 h. (C) Cellular distribution of the AhR in response to treatment with 100 μg/mL of the AHE or AHB in HCT116 cells. The cells were treated with 100 μg/mL of the AHE, 100 μg/mL of the AHB, 5 μM of SF, or 0.1 μM of 3-MC for 3 h, after which point an immunofluorescence assay was performed, followed by detection by confocal microscopy (bar=20 μm). The results represent the mean±SD; n=3. Asterisks denote significant differences compared to the control (*P<.05; **P<.01). EROD, 7-ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; 3-MC, 3-methylcolanthrene. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/jmf