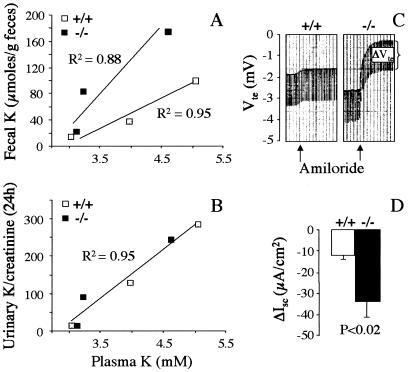
Figure 4.
Adaptation of fecal and urinary K+ excretion to varying K+ plasma levels and ion transport assessment in the colon of kcne1−/− and wild-type mice. (A and B) Colon and renal functions were estimated by plotting mean values of plasma K+ levels and fecal or urinary 24-h K+ excretion reached by the mice on the various K+ diets. The overall adaptation of the kidneys is not affected in kcne1−/− mice in contrast to the intestine whose dysfunction provokes a chronic K+ wasting in the feces. (C and D) Short circuit currents in colonic mucosa of kcne1−/− and wild-type mice. A typical recording is shown in C. Arrows indicate the application of 10 μM amiloride. The averaged amiloride-sensitive calculated short circuit currents (ΔIsc) are shown in D.