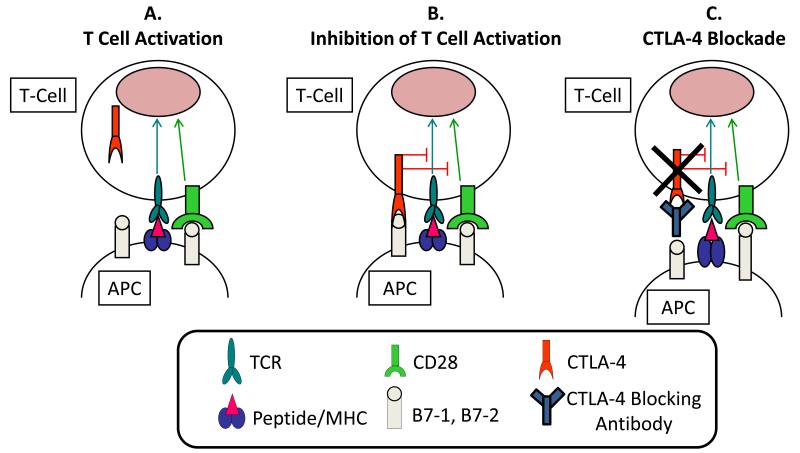
Figure 1.
Panel “A” shows T cell activation involves binding of the T cell receptor (TCR) to a peptide antigen bound to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on the surface of an antigen presenting cell (APC). This process also involves the interaction of CD28 on T cells with the B7 molecules on APC. Following T cell activation, panel “B” shows CTLA-4 is up-regulated and expressed on the cell surface of effector T cells and functions as an inhibitory molecule, outcompeting CD28 in the binding to B7, and causing inhibition of T cell activation and function. Antibodies that block CTLA-4 such as ipilimumab and tremelimumab bind to and inhibit the function of CTLA-4 and, thus, enhance T cell function as shown in panel “C”.