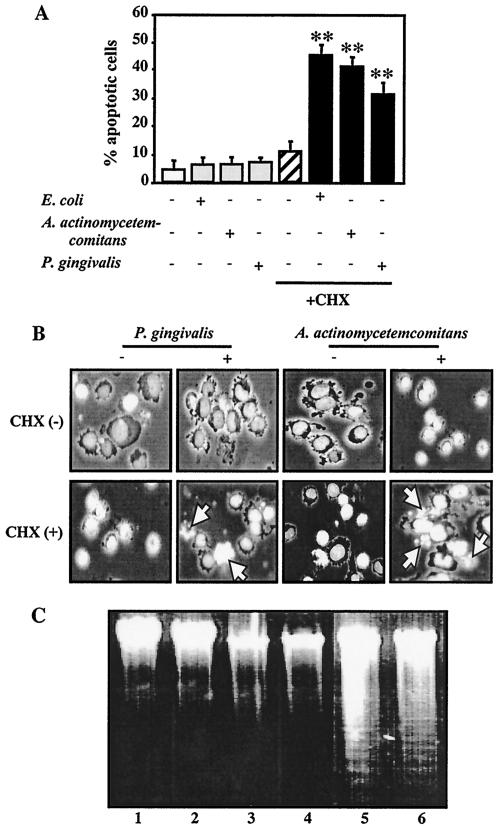
FIG. 2.
LPS-induced apoptosis of TPA-differentiated U937 cells in the presence of CHX. TPA-differentiated U937 cells (105 cells [A and B] or 107 cells [C]) were treated with a 1-μg/ml concentration of E. coli LPS, A. actinomycetemcomitans LPS, or P. gingivalis LPS in the presence or absence of CHX (10 μg/ml) for 3 h. Following each treatment, apoptosis in the cells was evaluated by morphological assessment using Hoechst 33258 dye (A and B) or analysis of DNA fragmentation (C), as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Values shown (percent apoptotic cells) are the means + SD (error bars) of three separate experiments, each conducted in triplicate. Differences from the value for untreated cells were considered significant (**) at a P of <0.01. (B) Morphological features of apoptotic cells (i.e., condensed and fragmented nuclei, cell shrinkage, and formation of apoptotic bodies). White arrow indicates apoptotic cells. (C) Agarose gel detection of DNA fragmentation. Lanes: 1 vehicle; 2, CHX alone; 3, A. actinomycetemcomitans LPS alone; 4, P. gingivalis LPS alone; 5, A. actinomycetemcomitans LPS plus CHX; 6, P. gingivalis LPS plus CHX.