Figure 10.
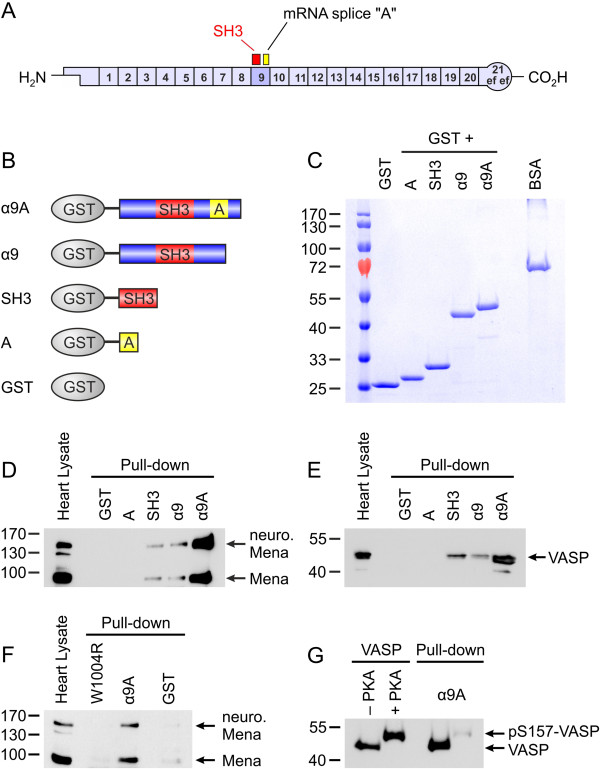
C-terminal extension of the αII-Spectrin SH3 domain enhances interaction with Mena and VASP. (A) αII-Spectrin is composed of 21 triple-helical repeats. Two αII-Spectrin splice variants exist in the mouse heart, either with or without a 20-amino acids insertion in the 9th repeat (“A”), C-terminal to the SH3 domain (indicated in red). The splice variant with the insertion is termed SH3i. (B, C) Schematic diagram (B) and Coomassie stained gel (C) of the purified GST-αII-Spectrin fusion proteins used for the pull-down experiments shown in D-G. Two microgram bovine serum albumin (BSA) served to calibrate the protein load. (D, E) Lysates of adult (D) and neonatal (E) mouse hearts were incubated with the depicted GST-fusion proteins and the precipitated material was blotted with Mena- or VASP-specific antibodies, respectively. (F) The interaction between Mena and SH3i, requires a functional SH3 domain and mutation of α9A to exchange the conserved Trp1004 residue with an arginine (W1004R) abrogates the binding. (G) The interaction between purified recombinant VASP and SH3i is regulated by phosphorylation. GST-α9A readily precipitated the non-phosphorylated VASP (46 kDa), but not PKA-phosphorylated protein (pS157-VASP, 50 kDa).