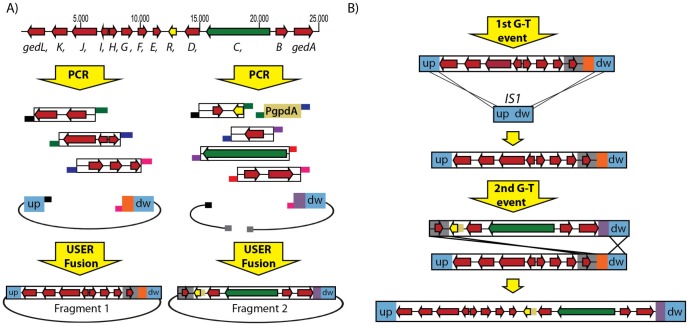
Figure 1. Schematic overview of the PCR based USER cloning strategy for transfer of entire gene clusters from one fungus to another.
In the illustrated case, the geodin gene cluster in A. terreus is PCR amplified, cloned, and integrated into the IS1 locus in A. nidulans. A) ORFs GedA-GedL are depicted as arrows. The yellow and green arrows represent the ORFs encoding the transcription factor and the PKS, respectively. Remaining ORFs are represented by red arrows. Arrow size is proportional to ORF length and arrow direction indicates genomic orientation. Numbers above the gene cluster specify sequence in base pairs. Genomic DNA fragments and cloning vectors are amplified as PCR products using primers extended with uracil-containing tails. The tails contain matching sequences (indicated by identical colors) allowing for PCR product assembly in a single USER Fusion reaction. For the geodin cluster, all putative ORFs are fused into two fragments, which are individually inserted into a vector prepared for gene targeting. Blue boxes labeled up (upstream) and dw (downstream) represent targeting sequences for homologous recombination into IS1 in the first gene-targeting event. The targeting sequences in the second integration event are represented in gray and blue and consist of the overlapping region between Fragment 1 and 2 and the downstream part of IS1, respectively. Genetic markers used for selection are depicted in orange (argB) and purple (AFpyrG). The sizes of uracil-containing tails, vector elements and PgpdA fragment are not drawn to scale. B) The first gene-targeting event introduces the first fragment into IS1 by homologous recombination between IS1 up and down-sequences as indicated. The second gene-targeting event introduces the second fragment using the overlapping region of the Fragment 1 and 2 (gray) and the downstream section of IS1 as targeting sequences. Note that additional DNA can be inserted in subsequent gene-targeting events. For example, a third fragment can be inserted by using the downstream end of fragment 2 and the downstream region of IS1 as targeting sequences. See text for details concerning use and recycling of markers.