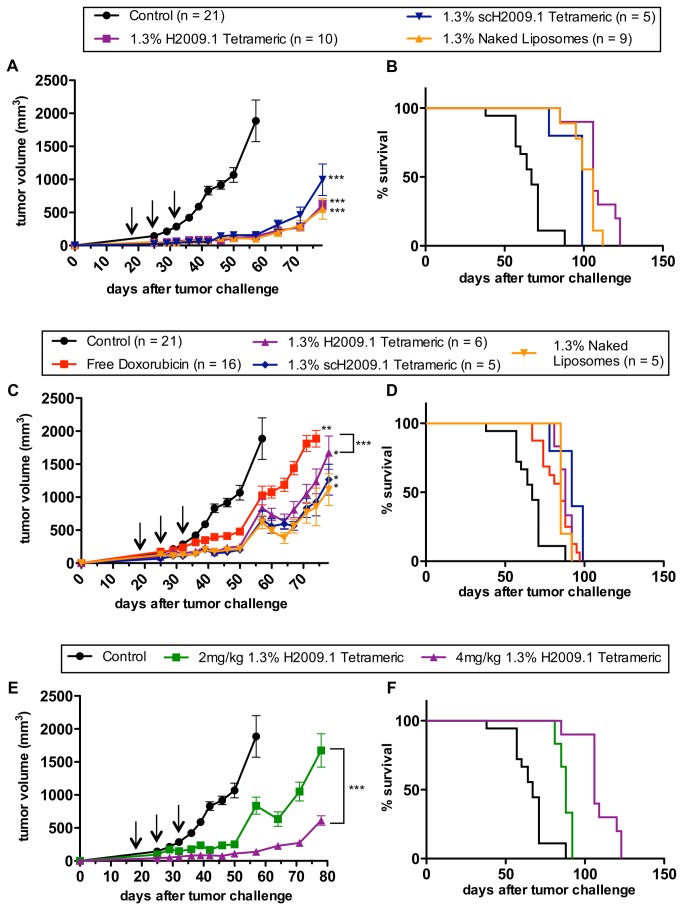
Figure 1. The 1.3% H2009.1 tetrameric liposomes inhibit tumor growth to the same extent as control liposomes.
Subcutaneous H2009 tumors were established in the flank of NOD/SCID mice. Tumor-bearing mice were treated with HBS (control) and either 4mg/kg (A–B) or 2mg/kg (C–D) of free doxorubicin or the 1.3% H2009.1 tetrameric, scH2009.1 tetrameric, or naked liposomes, based on the total concentration of doxorubicin. A) Tumor growth curves for mice treated with 4mg/kg of the different liposome formulations demonstrate that the αvβ6-targeting 1.3% H2009.1 tetrameric liposomes inhibit tumor growth to the same extent as the control scH2009.1 tetrameric and naked, no peptide, liposomes. (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for mice treated with 4mg/kg of the different liposome formulations demonstrate that all of the liposome treatments significantly increase survival compared to control mice (p < 0.0001 for the H2009.1 tetrameric and naked liposomes and p = 0.0007 for the scH2009.1 tetrameric liposomes), and treatment with the H2009.1 tetrameric liposomes increases survival compared to treatment with control scH2009.1 tetrameric liposomes (p = 0.0068). (C) Tumor growth curves for mice treated with 2mg/kg of the different liposome formulations demonstrate that free doxorubicin and all of the liposome formulations significantly inhibit tumor growth compared to control mice, and all 3 liposome formulations inhibit tumor growth to the same extent at levels significantly better than free doxorubicin. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for mice treated with 2mg/kg of the different liposome formulations demonstrate no significant survival difference between mice treated with either free doxorubicin or any of the liposome formulations. (E & F) Direct comparisons of the tumor growth (E) and survival (F) of mice treated with 4mg/kg or 2mg/kg of the 1.3% H2009.1 tetrameric liposomes demonstrates that the 4mg/kg treatment was significantly better at inhibiting tumor growth and significantly increased survival (p = 0.0005). Arrows indicate treatment days. *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001verses control, unless otherwise indicated with brackets.