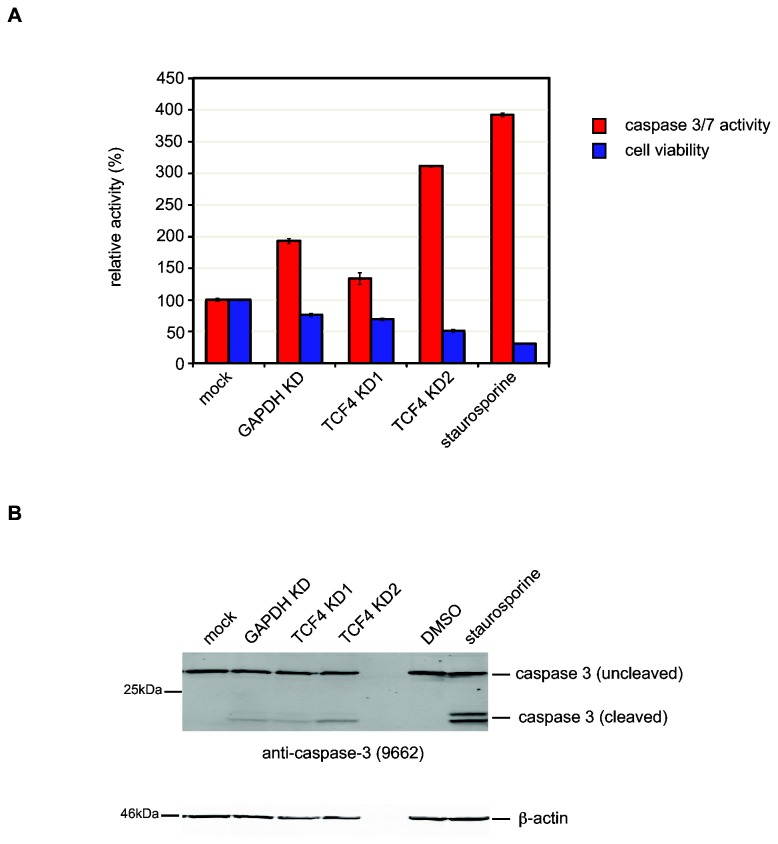
Figure 3. Knockdown of TCF4 induces apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells.
Cells were treated with siRNAs for 72h after which cell viability and caspase activity were measured (A). In addition to the siRNA treatment groups, untransfected SH-SY5Y cells were exposed to staurosporine (1µM in DMSO) and vehicle for 3h to induce apoptosis. Knockdown of TCF4 leads to a significant reduction in cell viability (P = 2.8x10-16, blue bars). Furthermore, TCF4-knockdown is also associated with an increase in caspase 3/7 activity compared to controls (P = 1.3x10-3, red bars). Although GAPDH knockdown is associated with reduced cell viability and elevated caspase 3/7 activity compared to mock-treated cells, both assays showed statistical significant differences between the control groups (mock and GAPDH) compared to TCF4-knockdown (TCF4 KD1 and KD2) supporting the microarray data. As expected, staurosporine treatment also reduced cell viability and increased caspase 3/7 activity in untransfected cells. Western blot analysis of caspase 3 processing after 72h knockdown shows that caspase 3 cleavage products are detected in siRNA treated cells (B). β-actin was used as a loading control for all treatment groups.