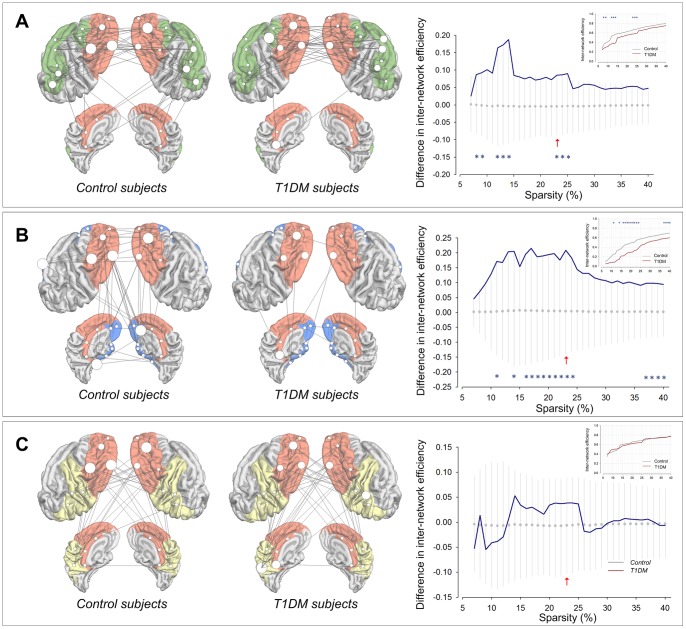
Figure 2. Connections and between-group differences in inter-network efficiencies.
Connections of cortical structural network for strategic/executive control with other networks mediating language (A), mnemonic/emotional processing (B), and sensorimotor function (C) and between-group differences in inter-network efficiencies are presented in the left and right panels, respectively. Brain templates in figures demonstrate cortical parcellated regions for corresponding intrinsic cortical structural sub-network systems and inter-network connections at the sparsity threshold of 0.23. Red arrows in graphs indicate the sparsity of 0.23 that whole-brain structural networks of both control and T1DM groups included all 64 connected brain regions. Hub regions shown in Figure 3 are marked as larger white circles with the radius in proportion of the value of Bi. The graphs showed the differences in average inverse shortest path length of submatrix for each corresponding intrinsic cortical structural network system between the T1DM and control groups (blue line). The mean values and 95% of confidence interval of the null distribution of between-group differences in parameters obtained from 1000 permutation tests at each sparsity level were represented as gray circles and error bars, respectively. Asterisks indicate significant differences in average inverse shortest path length between the T1DM and control groups at P<0.05. Inset graphs show average inverse shortest path length of submatrix representing inter-network efficiency, was plotted as a function of sparsity thresholds in T1DM (red line) and control (gray line) subjects. Abbreviations: T1DM, type 1 diabetes mellitus.