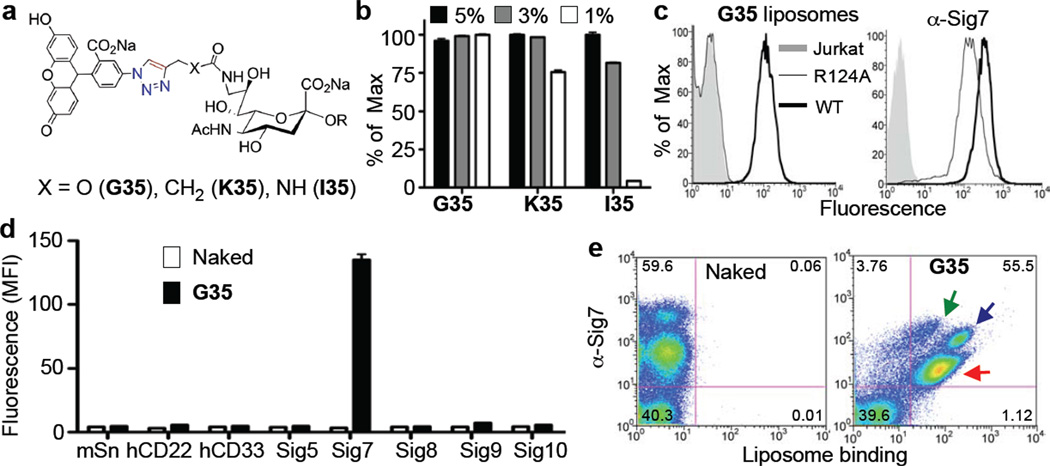
Figure 3. Avidity and selectivity of G35-liposomes for Siglec-7 expressing cells.
(A) The Siglec-7 hits G35, K35, and I35 were resynthesized, coupled to PEGylated lipids (Supporting Scheme 4), and formulated into liposomal nanoparticles at various ligand percentages. (B) These were then assessed for binding to Jurkat Siglec-7 expressing cells in triplicate. (C) The best ligand liposomes, G35-liposomes (1% ligand), were then assessed for binding to Jurkat (grey shaded), wild-type Jurkat Siglec-7 (dark black line), and R124A Jurkat Siglec-7 (thin black line) cells (top) to show that the essential Arg is critical for binding. As a control, an anti-Siglec-7 antibody was used (bottom). (D) The specificity of these liposomes (1% ligand) was then assessed against a panel of Siglec-expressing cell lines in triplicate. Naked (no ligand) liposomes were used as a negative control. (E) White blood cells from peripheral human blood were obtained and incubated with Naked or G-35 liposomes (5% ligand) followed by staining with an anti-Siglec 7 antibody showing that G-35 liposomes bind to all Siglec-7 positive populations (green arrow: lymphocyte subset, blue arrow: monocytes, red arrow: granulocytes), but not cells that are Siglec-7 negative.