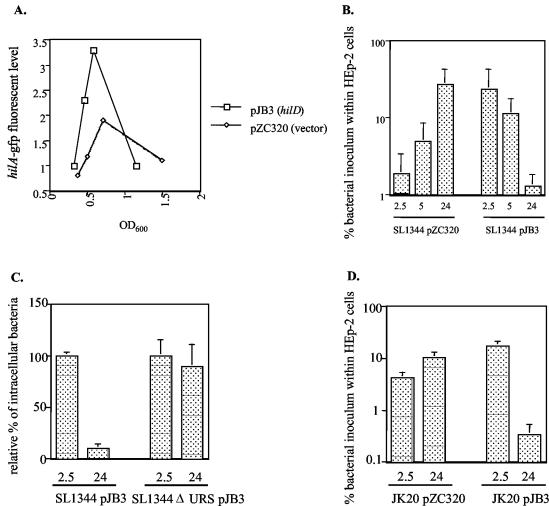
FIG. 3.
Plasmid expression of hilD increases bacterial invasion but decreases intracellular growth and survival. (A) Expression of hilA was estimated by determining the fluorescence level from Salmonella strain SL1344 pPhilA-gfp[ASV] carrying pJB3, which expresses hilD from the lac promoter, or the parent vector pZC320 at various times during a growth curve. The data shown are from one experiment that is representative of two separate experiments performed with similar results. (B) An invasion assay was performed with SL1344 containing pZC320 or pJB3 to determine invasion and intracellular survival of the bacteria from 2.5 to 24 h after infection. (C) Invasion and intracellular survival of SL1344(pJB3) and SL1344 ΔURS(pJB3) were determined. Since SL1344 ΔURS is noninvasive, the SL1344 ΔURS(pJB3) strain was coinfected with wt Salmonella that did not contain pJB3. The percentage of the original inoculum of each strain containing pJB3 that was recovered on LB-ampicillin plates after 2.5 h of infection was set to 100% for each strain, and the number of intracellular bacteria containing pJB3 at 24 h is reported as a percentage of that shown at 2.5 h. (D) Invasion and intracellular survival of the SPI-2 ssaV::cam mutant strain, JK20, carrying pZC320 or pJB3 after 2.5 or 24 h of infection. The invasion assay data are the mean plus the standard deviation of one experiment performed in triplicate that is representative of two or more independent experiments.