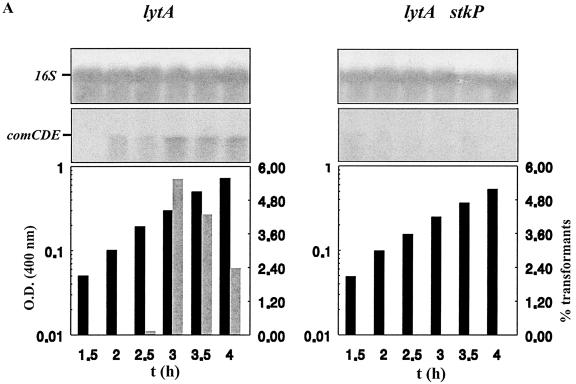
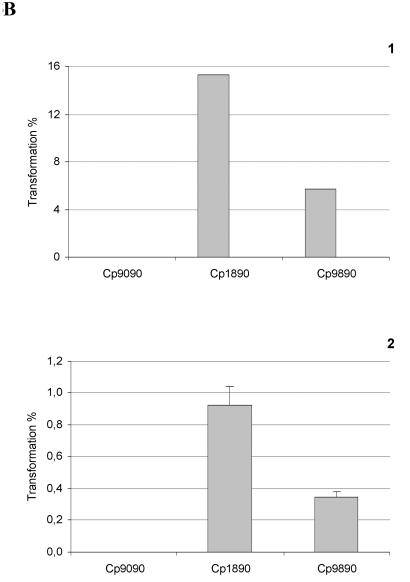
FIG. 3.
Positive control of comCDE mRNA cellular levels by StkP and impact on transformability in the wild-type and ciaR::spc genetic backgrounds. (A) Strains Cp1095 (lytA stkP+) and Cp9090 (lytA stkP) were grown aerobically in static flasks, and samples were withdrawn at 30-min intervals and analyzed for biomass increase (black bars), transformability (grey bars), and cellular levels of comCDE mRNA. Methods and material were as described in reference 8. The level of specific mRNA in cultures was evaluated by Northern blotting of total cellular RNA with the appropriate probes, and 16S rRNA was used as an internal qualitative and quantitative control. The columns representing growth, measured by comparing optical densities at 400 nm [O.D. (400 nm)], and transformability as the percentage of transformants (transformed by rifR chromosomal DNA) recovered relative to the total population are aligned with the Northern blot signals corresponding to the same culture. The experiment was repeated with independent cultures to test reproducibility. t, time. (B) The ciaR::spc mutation partially restores transformability of the stkP::aphA3 mutant strain. Both in situ transformation tests (4) (B1) and liquid transformation tests (8) (B2) were performed with strains Cp9090 (stkp::aphA3), Cp1890 (ciaR::spc), and Cp9890 (ciaR::spc stkP::aphA3). In panel B1, the data are expressed as the mean of results from two independent experiments, the results of which differed by less than 10%. In panel B2, the data are expressed as the mean of results from three independent experiments and the SEM is given.