Figure 1.
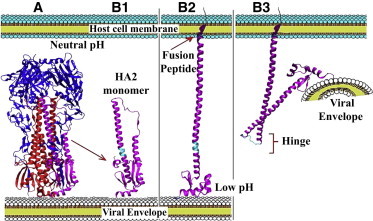
HA overall structure and functionally relevant conformational transitions. (A) Complete homotrimeric structure of HA including HA1 (blue) and HA2 (red; one HA2 chain highlighted in magenta). (B1–B3) A model for key structural changes in HA2 during the fusion process. (Cyan) Hinge region. (B1) HA2 monomer at neutral pH, with the fusion peptide locked in the HA2 core. (B2) Early low pH response including the release of the fusion peptide and its linking to the host cell membrane. (B3) Late low pH response, the bending of HA2 at the hinge (cyan), thereby placing the viral envelope very close to the host cell membrane.
