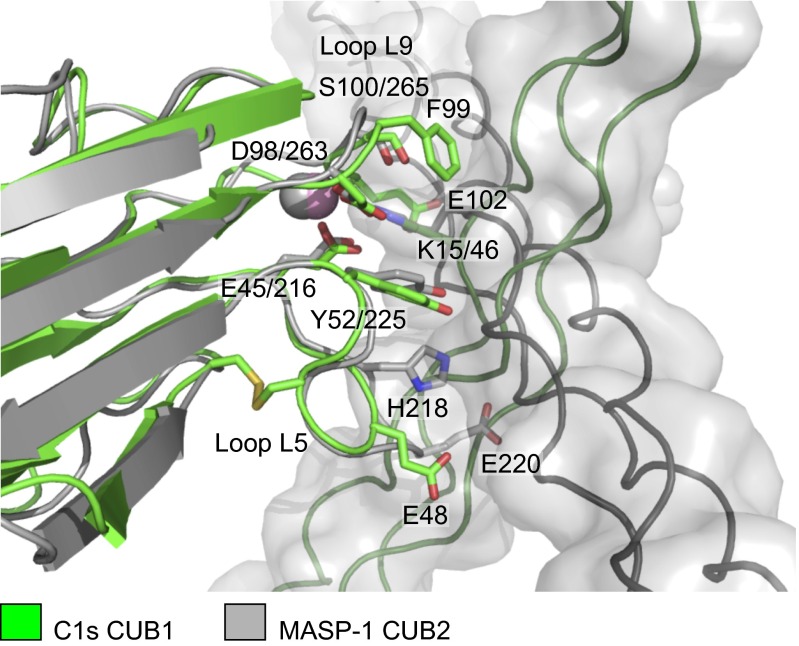
Fig. 2.
Comparison of CUB1–collagen and CUB2–collagen complexes of the classical and lectin pathways. Overlay of the C1s–C1q collagen structure (green) with the MASP-1/-3-MBL collagen structure (gray; PDB ID code: 3POB) (15). Key elements of the complexes superimpose including the lysine residue of the collagen, the Ca2+ and Ca2+-coordinating residues in the CUB domains together with a tyrosine residue, which contacts the collagen in each structure. However, the orientation of the collagen helices differs by ∼90°. Glu48 of loop L5 and Glu102 in loop L9 of C1s sandwich the collagen helix creating the shallow binding groove. Glu102 and other residues in loop L9 prevent binding in the alternative (horizontal) orientation through steric clashes. Loop L5 is longer in MASP-1 than in C1s and contributes toward binding via His218, which forms hydrogen bonds to the collagen, and blocks binding in the alternative (vertical) orientation (e.g., through Glu220, which would clash with the collagen chains).