Figure 1.
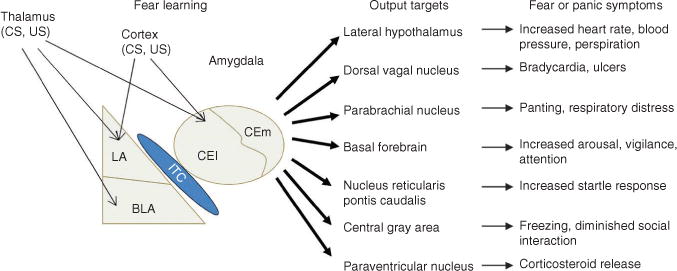
Schematic depicting the amygdala, the brain site most critical for fear learning. Information regarding the conditioned stimulus (CS) and unconditioned stimulus (US) is transmitted to the amygdala by way of sensory areas in the thalamus and cortex. Within the amygdala, the critical plasticity underlying the acquisition of fear conditioning is thought to occur in the lateral amygdala and the lateral portion of the central nucleus (CEl). The medial division of the central nucleus of the amygdala (CEm) projects to various brain areas that produce fear and panic symptoms seen in people with fear-related disorders. LA, lateral nucleus; BLA, basolateral nucleus; ITC, intercalated cells (see also ref. 99).
