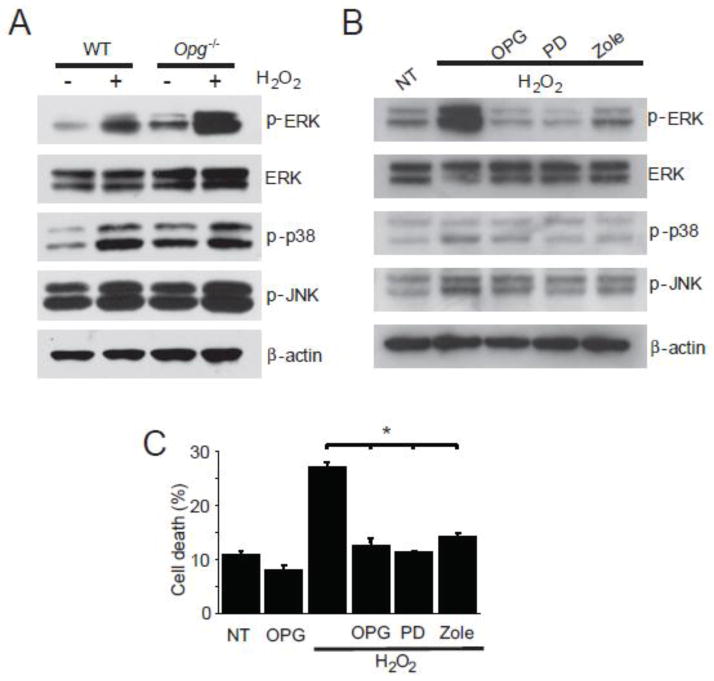
Figure 5. Sensitization of OPG deficient SGC to oxidative stress and apoptosis.
(A) After overnight treatment with 500 μM H2O2, Opg−/− SGC showed increased ERK activation, reflected in increased expression of phosphorylated ERK, which was substantially larger than ERK activation in the WT SGC. (B) Treatment of cultured Opg−/− SGC with H2O2 induced substantial ERK activation, while p38 and JNK activation was only slightly affected. ERK activation was suppressed by pre-treatment for 3 hours and co-treatment with either exogenous OPG (100 ng/L), the ERK inhibitor PD 98059 (PD, 20nM), or zoledronate (Zole, 10μM). This is a representative result from three replicates. (C) Exogenous OPG, the ERK inhibitor, and zoledronate rescued Opg−/− SGC from death. Pretreatment followed by co-treatment of SGC with OPG, PD 98059, or zoledronate rescued H2O2 induced oxidative cell death. NT: non-treated. The error bars indicate the standard errors of three replicates.