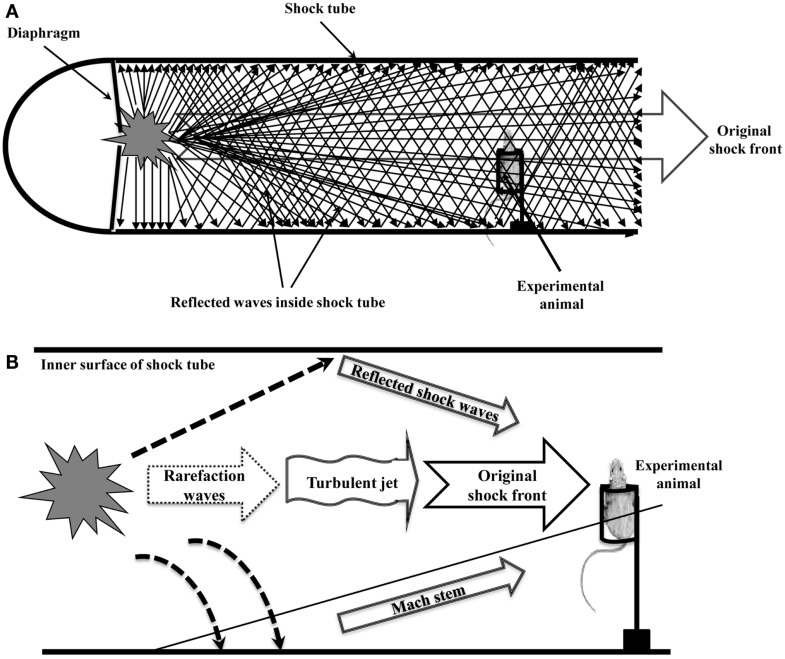
Figure 1.
Complex shock waves inside the shock tube. (A). A series of reflected shock waves are generated and reinforced when original shock front impinges on the inner surface of the shock tube. (B). Complex shock waves (including the original shock front, reflected shock waves, a Mach stem, an unsteady turbulent jet, and rarefaction waves) transfer kinetic energy to the experimental animal in shock tube, causing severe and complex blast injuries that are rarely observed in the blast victims.