Figure 4.
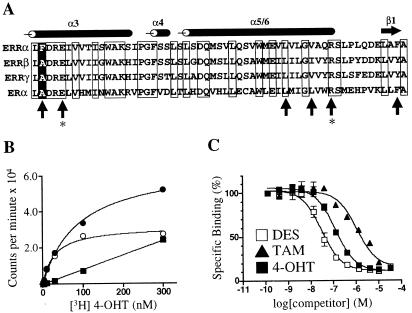
ERRαF232A has binding characteristics similar to those of ERRγ. (A) Alignment of the ERR and ER LBDs. The sequence begins with amino acid 231 for ERRα, 246 for ERRβ, 248 for ERRγ, and 349 for ERα. The positions of the α-helices and β-sheet are noted above the alignment. Conserved residues are boxed. Upright arrows indicate ER residues involved in recognition of DES and 4-OHT (26). The positions of glutamic acid-353 and arginine-394 in ERα, responsible for hydrogen bonding to the phenolic hydroxyl of the A ring of 4-OHT, are indicated by asterisks. The position of phenylalanine-232 in ERRα is indicated by a white letter on a black background. (B) Saturation binding curve of [3H]4-OHT and GST-ERRαF232A. The graph shows total (●), specific (○), and nonspecific (■) binding. Excess unlabeled 4-OHT (30 μM) was used to determine nonspecific binding. The Kd of 4-OHT was 40 nM. (C) Nonradioactive DES, TAM, and 4-OHT compete with [3H]4-OHT for binding to ERRαF232A. Ki values were 30 nM, 750 nM, and 110 nM, respectively. These data are from a single experiment preformed in duplicate. Two additional experiments gave similar results.