Figure 3.
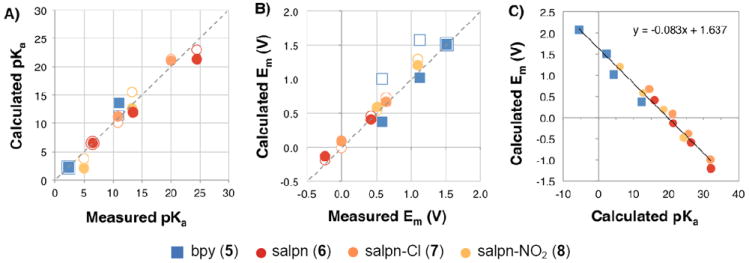
Calculated vs. experimental (A) pKas and (B) Ems for bpy (5), salpn (6), and dichloro- (7) and dinitro- (8) substituted salpns. Calculations use structures optimized in the Mn(III,IV) (filled symbols) and the Mn(IV,IV) (open symbols) states. Data from Figs. 4, 5, and Supplementary Information Table S1. Dashed lines show an ideal correlation through the origin with a slope of 1. (A) pKas: The best-fit line with the Mn(III,IV) optimized structures has a slope of 0.96, y-intercept of - 0.07 and R2 of 0.9. Using structures optimized in the Mn(IV,IV) state, the line has a slope of 1.20, y-intercept of 26 mV and R2 of 0.92. (B) Ems: The best-fit line with the Mn(III,IV) optimized structures has a slope of 0.99, y-intercept of -8 mV and R2 of 0.96. Using structures optimized in the Mn(IV,IV) state it has a slope of 0.77, y-intercept of 22 mV and R2 of 0.92. C) Correlation between Ems and pKas calculated with the Mn(III,IV) optimized structure for complexes 5-8 for oxidation or protonation reactions that increase the cluster charge by +1. Data is from Figs. 4 and 5. The best-fit line has a slope of -83 mV/pKa, y-intercept of 1.64 V and R2 of 0.97. All Ems in all panels are calculated in ACN. All pKas are in ACN except for complex 5, which is in water.
