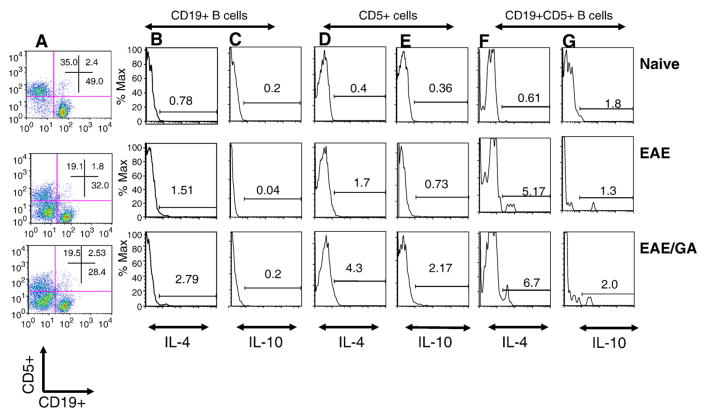
Fig. 1.
Administration of GA to EAE mice increases IL-4 and IL-10 expression by B cells. FACS of spleen and lymph node cells from C57BL/6 mice double-stained with antibodies against CD19+ and CD5+ cells and then intracellular cytokines IL-10 or IL-4. Naïve (n=4): untreated mice; EAE (n=4): EAE induced mice; EAE/GA (n=4): EAE induced mice treated with GA. (A) CD5+ cells (Y-axis) and CD19+ cells (X-axis) from gated lymphocytes; (B–G) Histograms showing the number of cells that express IL-4 (B, D and F) or IL-10 (C, E and G). (B–C) CD19 positive cells that express IL-4 (B) or IL-10 (C). (D–E) CD5 positive cells that express IL-4 (D) or IL-10 (E). (F–G) CD19+ CD5+ cells that express IL-4 (F) or IL-10 (G). Results shown are one representative of 4 independent experiments.