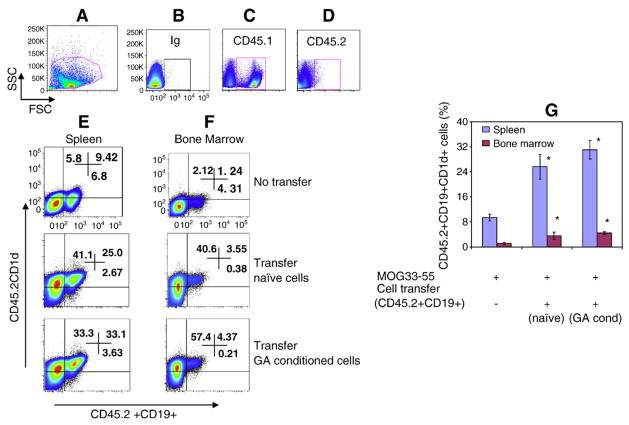
Fig. 2.
Recruitment of donor B cells to spleen and bone marrow of recipient mice in the presence of EAE. Sixty hours after intravenous injection of 10×106 CD19+ cells, genetically marked with CD45.2, into non-irradiated CD45.1 C57BL/6 mice, spleen and bone marrow of recipient mice were analyzed by FACS for the presence of CD45.2+CD19 cells. Data is presented as the percentage of CD45.2+CD19+ cells. A, representative figure of gating strategy, B, Ig control; C, CD45.1 expression in recipient mouse (Ly5.1, CD45.1, 90%) spleen cells; D, Donor cell (Ly5.2, CD45.2) expression in recipient mouse (Ly5.1, CD45.1, 0.1%) spleen cells; E, recipient mouse spleen cells expressing donor CD45.2+CD19+CD1d+ cells; F, recipient mouse bone marrow cells expressing donor CD45.2+CD19+CD1d+ cells; G, average data (%) from 3 mice/group. Asterisk (*) indicates statistical significance of cell transfer groups vs non-transfer group.