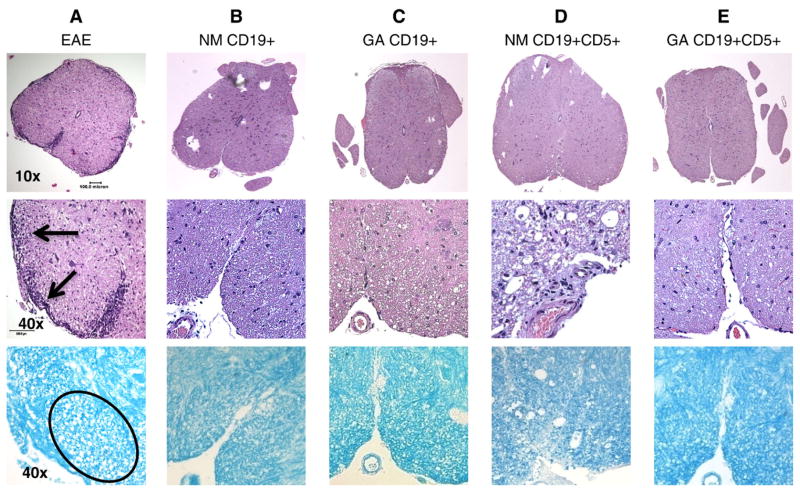
Fig. 4.
Minimal inflammation and tissue damage is evident in spinal cords from EAE mice treated with B cells. Representative lumbar spinal cord sections harvested 18 days after MOG immunization and B cell treatment stained with H&E and LFB. Upper panels are 10× magnifications (scale bar: 0.5 mm). Middle and lower panels are 40× magnifications (scale bar: 0.01 mm). Lowest panels are sections stained with LFB to indicate myelin, which appears blue. Spinal cords from: (A) Mouse that developed EAE showing severe infiltration of inflammatory cells and axonal damage; (B) EAE mouse that received CD19+ cells from naïve mice; (C) EAE mice that received CD19+ cells from GA conditioned mice; and (D) EAE mice that received CD19+CD5+ cells from naïve mice. (E) EAE mice that received CD19+CD5+ cells from GA conditioned mice. Similar results were obtained in at least 3 independent experiments.