Figure 1. Generation of a conditional Cxcr2 allele and genotype determination of conditional knockouts by PCR.
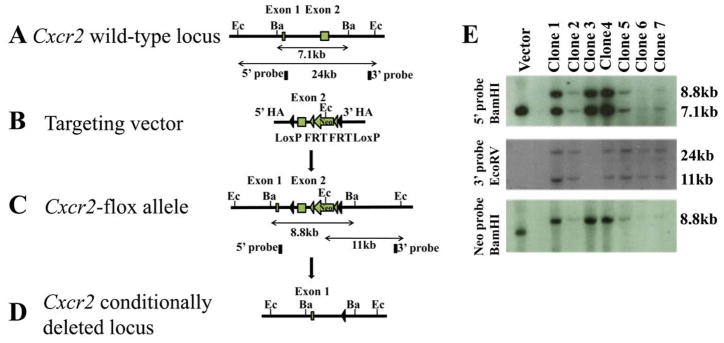
a. The strategy for Cxcr2fl mouse generation. (A). Schematic diagram of the Cxcr2 wild-type genomic locus demonstrating a classic two-exon gene structure that is indicated by two blank boxes. In order to screen for the targeted Cxcr2fl mutant allele, both 5′ and 3′ Southern blot probes (filled boxes) were designed in the genomic regions inside of two homologous arms (HA). Restriction enzymes are in the abbreviated form: Ec, EcoRV and Ba, BamHI. (B). A Cxcr2fl targeting vector was constructed by recombineering. The targeting region includes a 2-kb 5′ HA, a LoxP site that flanks Cxcr2 exon2, a Frt-PGKNeo-Frt cassette that is downstream of Cxcr2 exon2 flanked by another LoxP site and a 3-kb 3′ HA. (C). Schematic demonstration of the targeted Cxcr2fl allele. In Southern blot screening, an 8.8kb-BamHI targeted band (5′ probe) and an 11kb-EcoRV targeted band (3′ probe) are expected. (D). Schematic diagram depicting the conditional deletion of the Cxcr2 gene through Cre-mediated recombination. (E). Seven targeted embryonic stem cells were screened by Southern blot. 7.1kb wild-type and 8.8kb targeted BamHI bands were detected by the 5′ Southern probe. 24kb wild-type and 11kb mutant-type EcoRV bands are detected by the 3′ Southern probe. An 8.8kb targeted BamHI band is detected by using the PGK-neo probe. Targeting vector was used as the control. b. Genotype determination of Cxcr2-CKO mice by PCR. (A) Strategy for designing PCR primers to detect the Wt locus, the flox allele and the deletion of the flox allele. The primers are shown as arrows. (B) PCR amplification of the genomic DNA using primers for the flox gene before injection of poly(I:C); the higher band (~650 bp) indicates the wild-type allele and the lower band (~450 bp) indicates the flox allele (top). PCR amplification of the genomic DNA using primers to detect the deletion of the flox allele (~400 bp) after poly(I:C) induced recombination (bottom). (C) PCR amplification of the genomic DNA using primers to detect the Mx-Cre transgenes (top). The details for designing the primers specific for Mx-Cre are described in supplementary data 1. The bottom figure shows representive PCR results of GAPDH for quality control of the genomic DNA used for (B) and (C).
