Table 3.
Summary of chemical and biotechnologic properties of polymers used in drug delivery
| Structure | Properties |
|---|---|
1. Poly(glycolic acid)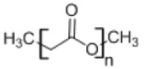
|
• Used as a matrix for controlled drug delivery and degradable sutures • Insoluble in organic solvents with high melting point52 |
2. Poly(lactic acid)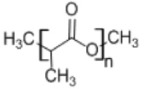
|
• Used in micelles of poly(ethylene glycol) to solubilize anticancer drugs168 |
3. Poly(caprolactone)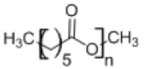
|
• Semicrystalline polymer with slow degradation rate • Drug delivery systems have been developed using biodegradable scaffolds7,169 |
4. Poly(lactide-co-glycolide)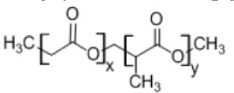
|
• Used as a matrix for controlled drug delivery • Mechanical and degradation properties can be tailored depending on the copolymer ratios4,7 |
| 5. Poly(ethylene glycol) |
• Most used biodegradable polymer for medical applications • Possesses flexibility, high aqueous solubility, and high circulation time • Enhances drug activity35,113,116 |
6. Poly(ortho ester) II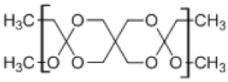
|
• Poly(ortho esters) consist of four-membered family of polymers; POE I, POE II, POE III, and POE IV • Used in controlled drug delivery • Degradation by erosion due to its hydrophobicity • Very stable under physiologic conditions7,170 |
7. Poly[(carboxyphenoxy)propane-sebacic acid]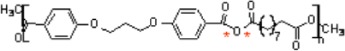
|
• Used in controlled drug delivery • Degradation by surface erosion • Produces minimal inflammatory reaction7,171 |
8. Poly(alkyl cyanoacrylate)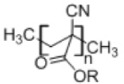
|
• Used in drug delivery • Has negative surface charge • Has low toxicity • Easy to prepare • Polymerization requires a pH below 3.564 |
9. Desaminotyrosyl octyl ester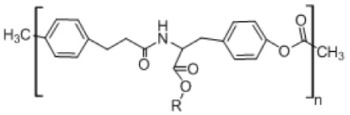
|
• Enhances the penetration of lipophilic molecules into the skin • Forms stable complexes with anticancer drugs • Retains the biological activity of drugs in in vitro studies165 |
10. Polyphosphoesters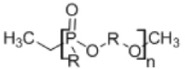
|
• Suitable for controlled release of drugs • Good tissue compatibility and minimal lymphocyte or macrophage activity • Degradation by hydrolysis or enzymatic cleavage of the phosphate in the polymer chain32 |
11. Polyester amides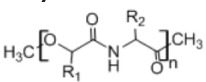
|
• Used in controlled drug delivery, hydrogel formulations, and tissue engineering, and as adhesive material • Provides good mechanical and thermal characteristics43 |
| 12. Polyurethanes |
• Widely used in biomedical applications such as heart valves, cardiac catheters, scaffolds, ligament reconstructions, controlled-release drug systems46 |
13. Chitosan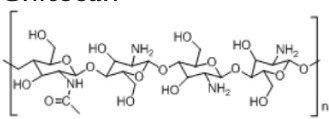
|
• Used in controlled drug release and scaffolds • Has a cationic character based on its primary amino groups, and can be cross-linked using several cross-linking agents172,173 |
Note: *Hydrolyzable sites.
Abbreviation: POE, poly(ortho ester).
