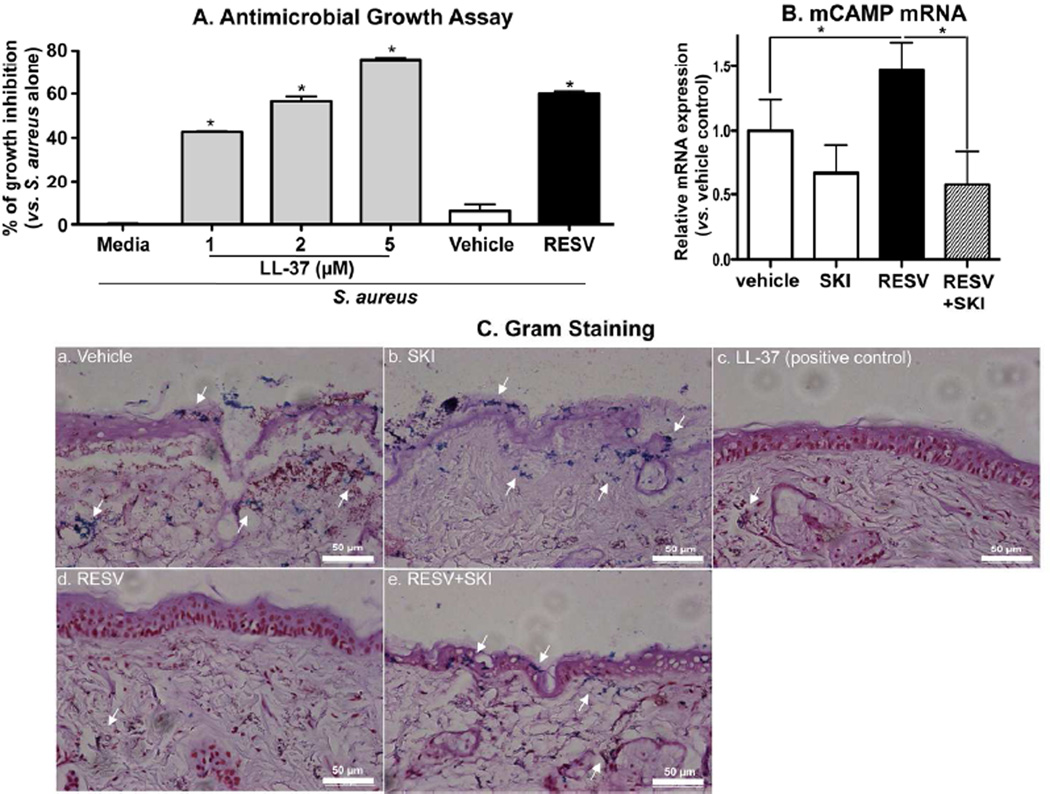
Figure 4.
RESV enhanced antimicrobial defense through increased CAMP production: Growth inhibition of S. aureus. S. aureus were incubated for the indicated times with LL-37 or conditioned medium of HaCaT KC treated with RESV (50 µM) (A). Bacterial invasion studies (ex vivo) (B and C): S. aureus were epicutaneously applied to a full-thickness pieces of murine skin (n=2) treated with RESV (50 mM [250 nmole/cm2]), SKI (1 µM), LL-37 RESV (50 µM [250 pmole/cm2]) and/or vehicle twice daily for 3 days, followed by incubation for 24 h at 37°C. CAMP mRNA expression in skin was assessed by qRT-PCR (B). Bacterial invasion/growth into murine skin was assessed by gram staining (counter staining with H&E) (C). Scare bar = 50 µm.