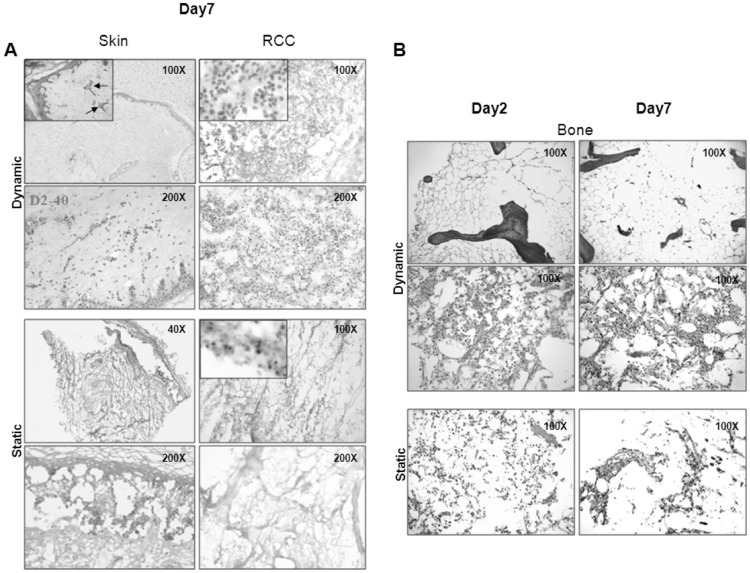
Figure 1. 3-D culture in the RCCS™ bioreactor preserves cellularity and tissue histo-architecture.
A. Left: skin explants from healthy donors were cultured in the RCCS™ bioreactor (upper panels) and in static conditions (lower panels) for seven days. Epidermal and dermal strata and annexes are well preserved and vessels, both blood (insert, arrows) and lymphatic (D2-40) are identifiable in dynamic conditions (upper panels), while histo-architecture is completely disrupted in static conditions (lower panels). Right: RCC samples cultured for seven days in Bioreactor (upper panels) showed maintenance of cellularity and viability (insert); both features were lost in parallel cultures under static conditions (lower panels). B. Bone explants from an elderly (upper panels) and a 14-year-old (middle panels) healthy control were cultured in Biorector; samples were retrieved at the indicated time points and submitted to H&E staining. BM from the elderly patient is physiologically depleted of hematopoietic components, and replaced by adipose tissue. Bone trabeculae are also evident (upper panels). BM from a young donor displays a substantial cellularity, represented by hematopoietic elements and adipocytes in the context of abundant stroma (middle panels). In parallel, bone explants from the young donor, cultured in conventional static conditions, display progressive loss of both cellular and stromal components, resulting in disruption of overall architecture (lower panels). Original Magnification (OM) 200X.