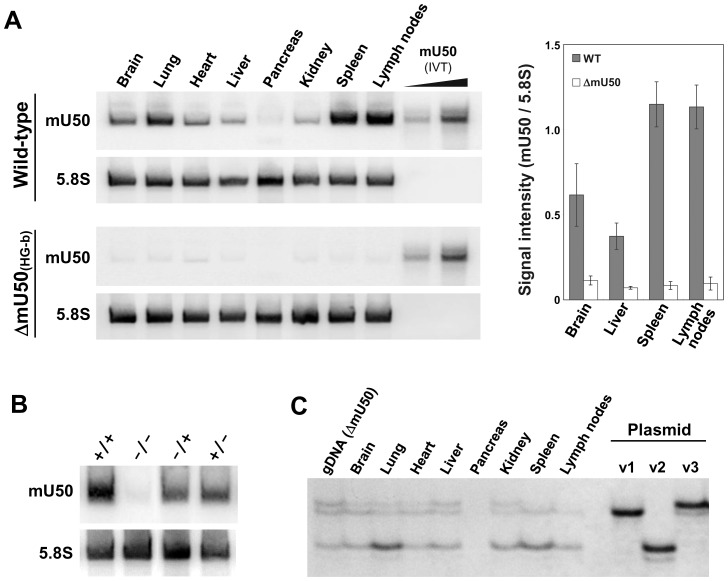
Figure 3. Molecular aspects of different organs in ΔmU50(HG-b) and wild-type mice.
(A) Northern blot analysis of mU50 snoRNA expression in eight organs from wild-type and ΔmU50(HG-b) mice. In vitro transcribed (IVT) mU50 snoRNA was applied as a control. Detection of 5.8S rRNA was performed for the loading control. The signal intensities of selected organs are indicated in the panel on the right of the Figure. (B) Northern blot analysis of mU50 snoRNA and 5.8S rRNA expression in spleen obtained from wild-type (+/+), ΔmU50(HG-b) (−/−), and maternally (−/+) and paternally (+/−)-inherited ΔmU50(HG-b) heterozygotes. (C) PCR-SSCP analysis of the mU50 snoRNA variants in ΔmU50(HG-b) mice. Genomic DNA from ΔmU50(HG-b) mouse, which contains a single copy of each mU50HG-a paralog, was used as the control PCR template. gDNA: genomic DNA; v1, v2 and v3: plasmids that correspond to the mU50 snoRNAs encoded by mU50HG-a(1), -a(2), and -a(3), respectively.