Figure 3.
Pseudogenization of B-Located Gene Fragments.
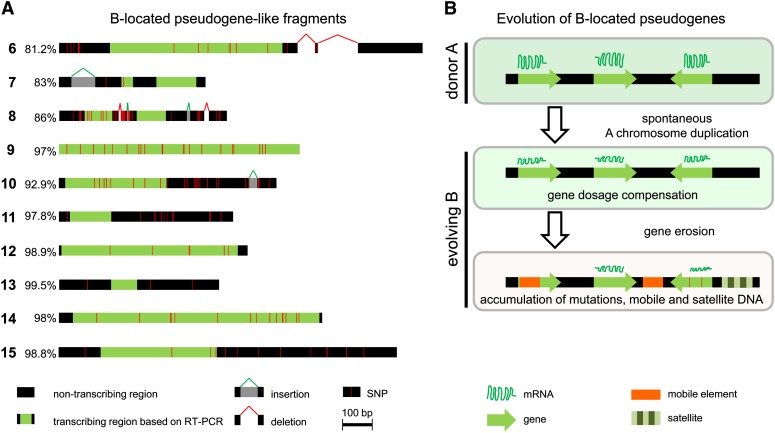
(A) Schemata represent the sequence comparison between rye B-located pseudogene-like fragments (6 to 15) and their A-located parental counterparts. Percentage of similarity, transcribing region, and position of sequence polymorphisms are indicated.
(B) Model for the evolution of B-located pseudogenes. The B of rye descended from As after a spontaneous whole or partial genome duplication. Meiotic recombination of proto-B with donor As became restricted. Proto- B still shows sequence similarity to the parental As. The increased gene dosage may affect gene expression and proto-B-located genes might have been suppressed by, for example, dosage compensation. Finally, B-located gene sequences became pseudogenized by mutations and accumulation of mobile and satellite DNA.