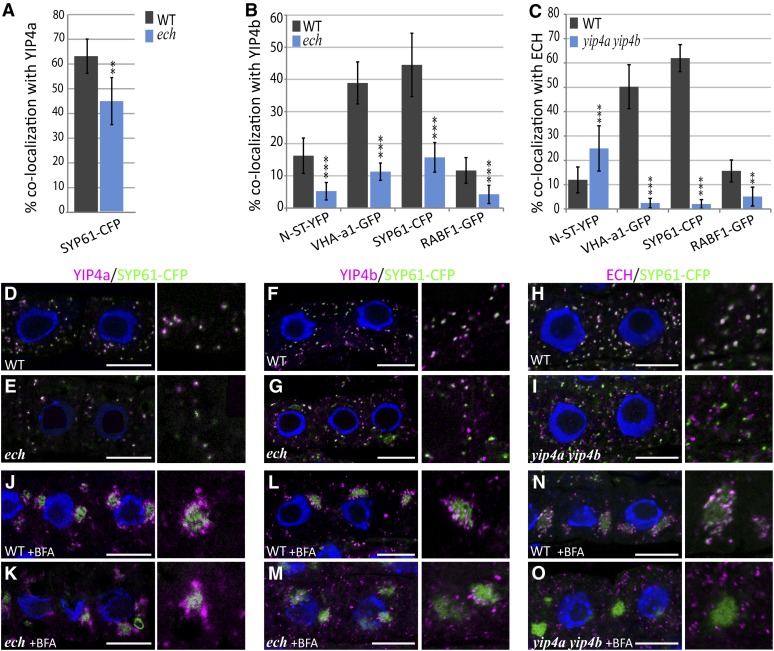
Figure 4.
ECH, YIP4a, and YIP4b Are Dependent on Each Other for TGN Localization.
(A) to (C) Quantitative measurement of colocalization of YIP4a (A), YIP4b (B), or ECH (C) with various markers in wild-type (WT; gray bars) or mutant (blue bars) root epidermal cells (n = 10 roots with four cells, average ± sd). Significant differences are indicated as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 (t test).
(D) to (O) Representative images are displayed in Supplemental Figure 4 online and in (D) to (O) for colocalization with SYP61-CFP. Colocalization of anti-HA (YIP4a; [D], [E], [J], and [K]) anti-YIP4b ([F], [G], [L], and [M]) or anti-ECH ([H], [I], [N], and [O]) labeling (magenta) with SYP61-CFP (green) without treatment ([D] to [I]) or after 1 h treatment with 50 µM BFA ([J] to [O]) in the wild type ([D] to [H] and [J] to [N]) or mutant ([E] to [I] and [K] to [O]). The 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole–stained nuclei are blue. Bars = 10 µm.