Figure 1.
R Light Induces Rapid Enhancement of Multisite Phosphorylation in PIF3 in Vivo.
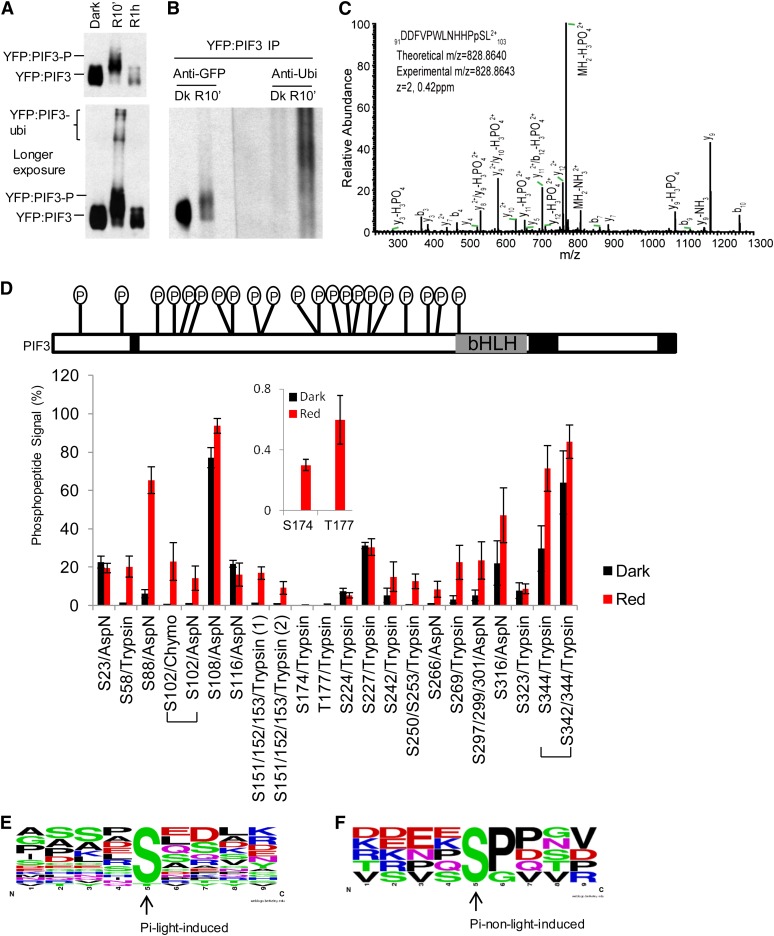
(A) Top panel: YFP:PIF3-N507 protein from dark (Dk)-grown transgenic Arabidopsis seedlings undergoes rapid light-induced mobility shift (phosphorylation) and degradation similar to native PIF3. Dark-grown YFP:PIF3-N507-expressing transgenic Arabidopsis seedlings were either kept in the dark or given a saturating R light pulse, then moved into darkness for a total time of 10 min or 1 h before protein extraction and immunoblot with GFP antibody. Bottom panel: YFP:PIF3-N507 protein was also detected in the very high molecular weight region (likely polyubiquitinated product) after a longer autoradiograph exposure time.
(B) Immunoblot against ubiquitin shows that light induces rapid YFP:PIF3-N507 phosphorylation (mobility shift; left panel [anti-GFP]) and polyubiquitination (high molecular weight region; right panel [anti-Ubi]) in the transgenic seedlings. YFP:PIF3-N507 protein was affinity purified with polyclonal GFP antibody and then blotted with either monoclonal GFP antibody (anti-GFP) or with ubiquitin antibody (anti-Ubi). Transgenic seedlings were grown and treated with R light (10 min) as in (A). IP, immunoprecipitation.
(C) Collision-induced dissociation mass spectrum showing phosphorylation of Ser-102, a light-induced phosphorylation site in PIF3. YFP:PIF3-N507 protein from transgenic plants was affinity purified as in (B) before being subjected to in-gel digestion with AspN.
(D) The phosphopeptide signal increases rapidly in response to R light exposure of seedlings. Top panel: Distribution of all phosphorylation sites identified in PIF3. The total mass spectrometry peptide coverage for PIF3 is ∼85% (uncovered regions are marked with back boxes). Bottom panel: Comparison of phosphopeptide signal (%) for PIF3 from dark control and R light–exposed (red 10 min) seedlings. The signal of the phosphopeptide containing a given phosphorylation site is expressed as the ion intensity of the phosphopeptide divided by the total ion intensity signal for this peptide (unmodified + phosphorylated) × 100 (see Supplemental Figure 1C online). The values do not represent absolute phosphorylation stoichiometries, but the relative percent values for R versus dark samples do correspond to the change in phosphorylation stoichiometry between these dark and R light–treated samples (red 10 min). Peptides were derived from in-gel digestion with trypsin, chymotrypsin (chymo), or AspN. Data are represented as the mean of biological triplicates ± se. Inset: Two light-induced sites with low phosphopeptide signal values.
(E) and (F) No strict consensus motif was identified for either light-induced (E) or non-light-induced (F) PIF3 phosphorylation sites using Weblogo. The middle Ser or Thr is the phosphorylation site.