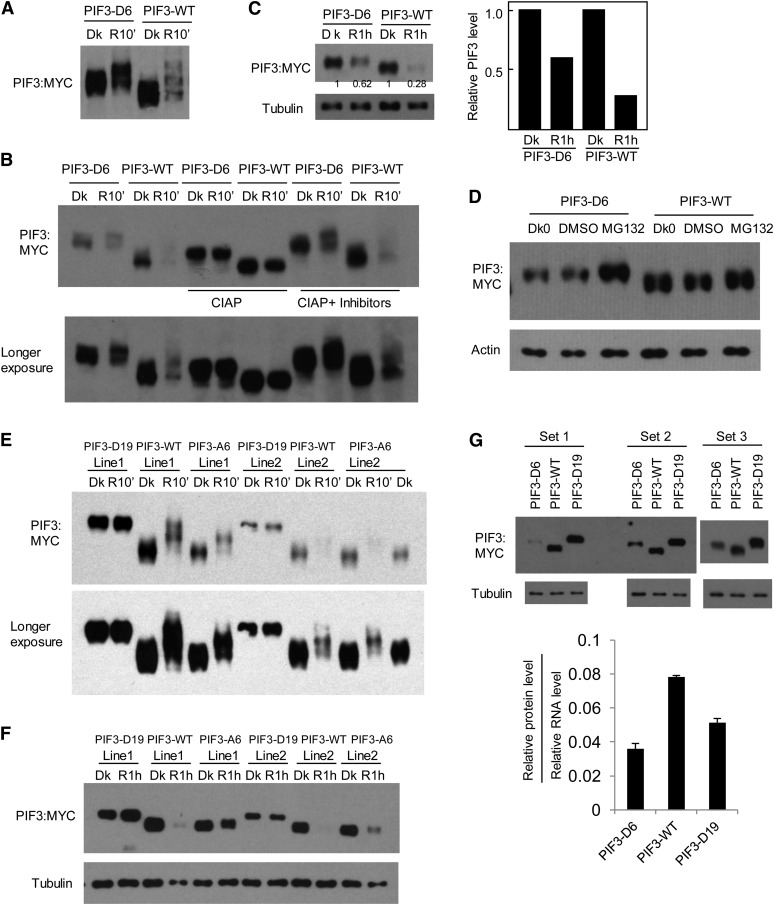
Figure 5.
Phosphomimic Mutations of a Subset of Strongly Light-Induced Phosphorylation Sites in PIF3 Promote Its Degradation in Vivo in the Absence of Light.
(A) PIF3-D6 exhibits a mobility shift in the dark (Dk) in transgenic Arabidopsis compared with the PIF3-WT control. Seedlings of transgenic lines expressing PIF3-D6:MYC or PIF3-WT:MYC fusion proteins were grown for 2.5 d in darkness, then either kept in the dark or given a saturating R light pulse and returned to darkness for 10 min before extraction into denaturing buffer and immunoblot analysis using MYC antibody.
(B) The same protein extracts as in (A) were treated with calf intestine alkaline phosphatase (CIAP) or phosphatase plus phosphatase inhibitors (CIAP + inhibitors) before immunoblot analysis.
(C) PIF3-D6 exhibits less light-induced degradation than the PIF3-WT control. Seedling growth, light treatment, and immunoblot analysis were as in (A), except that proteins were extracted at 1 h after light treatment and compared with those from dark samples. Tubulin was used as a control. Numbers directly on the blot image denote the relative PIF3 protein levels normalized to tubulin. Right panel shows quantification of relative PIF3 protein levels (normalized to the dark level set as 1).
(D) PIF3-D6 proteins are degraded through the 26S proteasome–mediated pathway in the absence of light. The 2.5-d-old dark-grown (Dk0) PIF3-D6:MYC– or PIF3-WT:MYC–expressing seedlings were treated with proteasome inhibitor MG132 or DMSO for a further 4 h in the dark before extraction and immunoblot analysis using antibodies against the MYC-epitope tag or against actin as a control.
(E) and (F) Light-induced mobility shift and degradation analysis of the PIF3-D19 and PIF3-A6 proteins from transgenic plants.
(E) Phosphomimic mutations of all light-induced sites identified in PIF3 (PIF3-D19) generate a mobility shift of the protein in the dark, similar to that induced by light at 10 min in the PIF3-WT protein, and no additional light-induced phosphorylation is observed. By contrast, the PIF3-A6 mutant protein exhibits reduced light-induced phosphorylation compared with PIF3-WT.
(F) The PIF3-D19 protein shows no apparent light-induced degradation, whereas the PIF3-A6 variant exhibits reduced light-induced degradation. Light treatment and immunoblot analysis were as in (A) and (C).
(G) PIF3-D6 and PIF3-D19 protein levels are lower than that of PIF3-WT after normalization to their corresponding RNA levels. Top panels: Triplicates of biological protein samples from 3-d-old dark-grown seedlings of the PIF3-D6, PIF3-WT, and PIF3-D19 were assayed by immunoblot using MYC antibody. Tubulin was used as a loading control. Bottom panel: Relative PIF3 protein levels after normalization to the corresponding RNA levels. Data represent the mean of biological triplicates ± se.